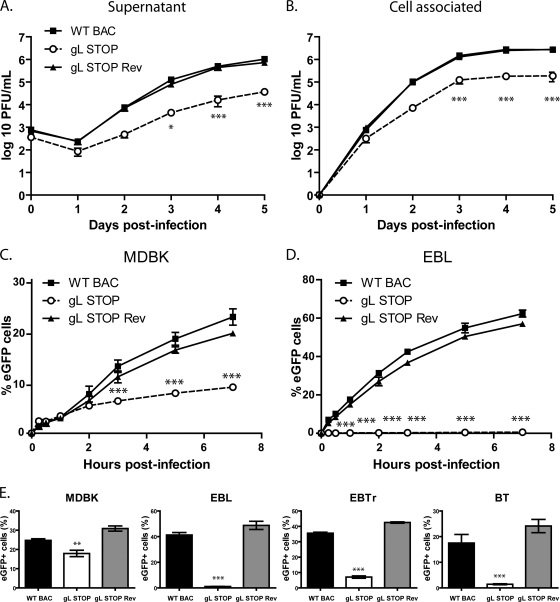
Fig 4.
A lack of gL causes a growth deficit associated with a defect in entry. (A and B) MDBK cells were infected with wild-type (WT BAC), gL STOP, and gL STOP Rev BoHV-4 strains in 6-well cluster dishes at an MOI of 0.01 PFU per cell. Supernatant of infected cultures (A) and infected cells (B) were harvested at different times after infection, and the amount of infectious virus was determined by plaque assay on MDBK cells. These plaques were visualized with eGFP and counted. The data presented are the averages of triplicate measurements ± standard deviations and were analyzed by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Bonferroni posttests (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001). For supernatants, time zero postinfection is retitration of the inocula to ensure that similar amounts of virus were put on the cells. (C and D) MDBK (C) or EBL (D) cells were exposed to eGFP-expressing wild-type (WT BAC), gL STOP, or gL STOP Rev BoHV-4 strains (0.4 PFU/cell) for the times indicated and then washed with PBS and cultured overnight in the presence of phosphonoacetic acid (PAA; 300 μg/ml). Eighteen hours after the virus was added to the cells, viral infection was assayed by flow cytometry for eGFP expression. The data presented are the averages of triplicate measurements ± standard deviations and were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni posttests (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001). (E) MDBK, EBL, BT, and EBTr cells were exposed to eGFP-expressing wild-type (WT BAC), gL STOP, or gL STOP Rev BoHV-4 strains (0.4 PFU/cell) and cultured overnight in the presence of PAA (300 μg/ml). Eighteen hours after the virus was added to the cells, viral infection was assayed by flow cytometry for eGFP expression. The data presented are the averages of triplicate measurements ± standard errors of the means and were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni posttests (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).