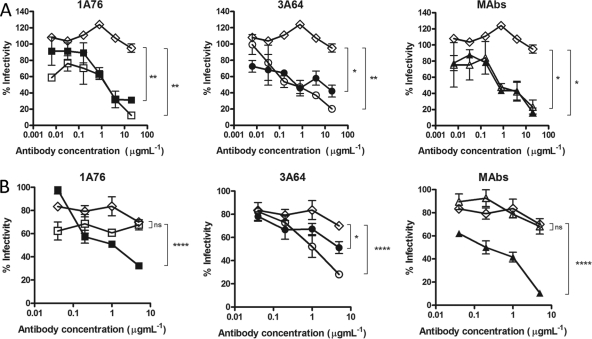
Fig 6.
Human and murine antibodies that target regions of E2 encompassing aa 412 to 423 and aa 434 to 446 neutralize HCVcc infection. Dilutions of 1A76 peptide I-Ig (■), 3A64 peptide I-Ig (●), 1A76 peptide II-Ig (□), 3A64 peptide II-Ig (○), MAb AP33 (▲), or MAb 2/69a (△) were used to neutralize the infectivity of H77c HCVcc (A) or JFH-1 HCVcc (B). As for the HCVpp assays, two different negative controls were used in these assays (♢): a normal human serum sample mock purified using the magnetic bead process was used as a negative control in the Ig neutralization assays, whereas HIV-1-specific monoclonal antibody 2F5 was used as a negative control in the MAb neutralization assays. Although neutralization assays were performed at the same time, for clarity, they are plotted on two panels corresponding to each peptide Ig and a third panel for the monoclonal antibodies. The same negative-control NHS data set is included in both Ig panels. The mean infectivities observed at the highest concentrations of each test antibody and the negative-control antibody were compared by using a t test. P values are indicated as follows: ns, P > 0.05; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001.