Fig 4.
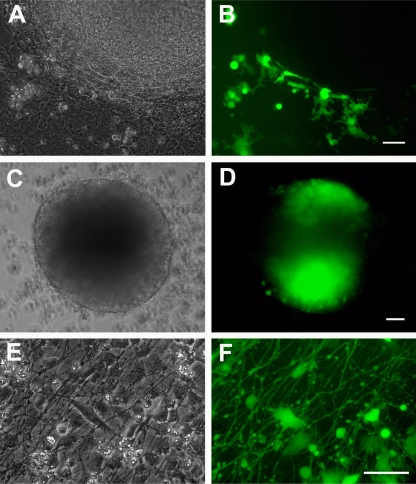
Neurospheres in suspension are the first stage of neural differentiation of hESC that support infection by VZV. (A and B) hESC cells were plated on PA6 stromal cells and differentiated for 14 days (shown diagrammatically in Fig. 1II). Mitomycin-treated VZV-GFP-infected MeWo cells were added to the coculture 10 to 12 days after hESC plating. Panels A and B show an hESC colony from a 14-day coculture with adjacent GFP-expressing MeWo cells. (The PA6 cells are murine and are not infected by VZV.) The neurally differentiating hESC colony is devoid of fluorescence. (C and D) hESC were cocultured with PA6 for 14 days as in panels A and B, and colonies were cut out and placed in suspension culture with VZV-GFP-infected MeWo cells (Fig. 1III). Three days postinfection, most of the neurospheres express GFP, indicating infection. (E and F) Neurospheres generated as described above were plated on laminin-coated coverslips and VZV-GFP-infected MeWo cells were added to the cultures immediately after adhesion of the neurosphere cells (Fig. 1IV). Three days after plating, the culture is a mixture of neural precursors and differentiated neurons bearing an extensive plexus of neurites. VZV infection of the neural cells is readily observed by GFP expression driven by an SV40 promoter. GFP diffusely fills the neurites and neuronal cell bodies. Panels A, C, and E are phase-contrast images, and panels B, D, and E are fluorescence images. Scale bars, 100 μm.