Fig 1.
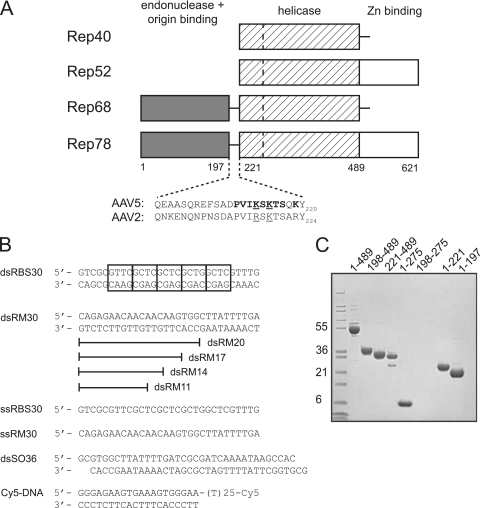
AAV Rep proteins and oligonucleotides used. (A) Schematic view of the domain organization of the AAV Rep proteins with amino acid numbering for the AAV5 serotype. The dashed line in the helicase domain represents the boundary between a four-helical bundle and the AAA+ domain. The residues comprising the domain linker region are shown for AAV5 and AAV2. Residues mutated in the present study are indicated in boldface: mutant 1 (K213A/K215A/K219A), mutant 2 (P210A/V211A/I212A/K213A), mutant 3 (S214A/K215A/T216A/S217A), and mutant 4 (K213A/S214A/K215A). Underlined residues are those mutated by Urabe et al. (46). (B) Oligonucleotides used for in vitro binding studies and the helicase assay. Cy5 indicates the fluorescent label appended to the 3′ single-stranded DNA end of Cy5-DNA. The boxes in dsRBS30 correspond to tetranucleotide repeats of the AAV5 Rep Binding Site (RBS). (C) SDS-PAGE analysis of AAV5 Rep proteins used. The gel was stained with Coomassie blue, and the molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) on the left side are Mark12 standards from Invitrogen.