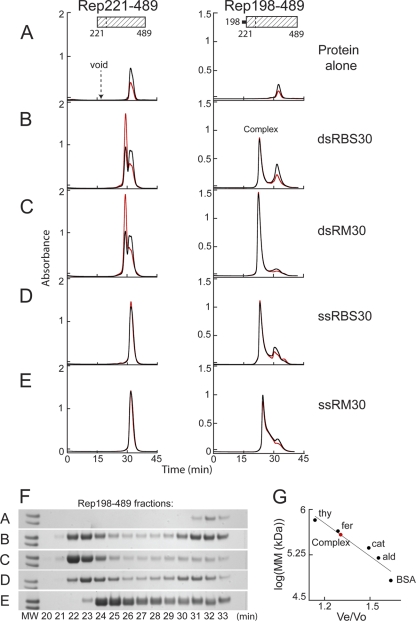
Fig 2.
The Rep helicase domain binds DNA when the linker region is appended. Binding was assessed on a Superdex 200 column based on comigration of protein and DNA during SEC after Rep221-489 (left) or Rep198-489 (right) at 82 μM (2.5 and 2.8 mg/ml, respectively) was mixed with a 6:1.2 molar ratio of the indicated DNA oligonucleotides and then dialyzed overnight in binding buffer (see Materials and Methods). The resulting chromatograms are shown in panels B to E. Protein alone similarly dialyzed is shown in panel A. Note that Rep198-489 is markedly less soluble than Rep221-489 in binding buffer. The A260 is shown in red, the A280 is shown in black, and the elution position of blue dextran (corresponding to the column void) is marked. The complex at ∼22.5 min that is formed with Rep198-489 is indicated. (F) SDS-PAGE of Rep198-489 fractions collected during chromatography; the indicated fraction number corresponds to the elution time in minutes. The two molecular weight (MW) markers on the left of each gel (Mark12; Invitrogen) represent Mr values of 36,000 (top) and 31,000 (bottom). (G) Standard curve used to determine the apparent molecular masses (MM) of Rep198-489/DNA complexes. The elution positions on a Superdex 200 column of the molecular mass standards (•) thyroglobulin (thy; 669 kDa), ferritin (fer; 443 kDa), catalase (cat; 232 kDa), aldolase (ald; 158 kDa), and bovine serum albumin (BSA; 67 kDa) are plotted on a semilog plot as log(MM) versus Ve/Vo, where Ve is the elution volume and Vo is the void volume elution time. The curve yields an apparent molecular mass of ∼385 kDa for the Rep198-489 complexes eluting at ∼22.5 min (red circle).