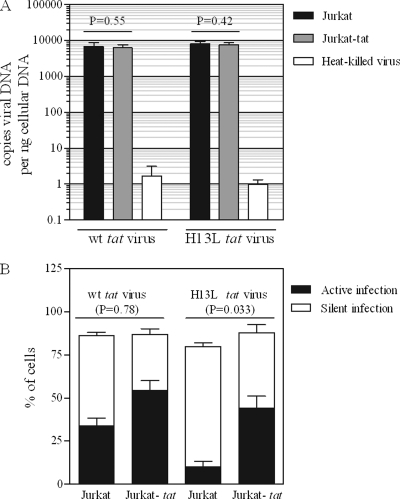
Fig 4.
Jurkat and Jurkat-tat cells are equally susceptible to viral infection. (A) Jurkat or Jurkat-tat cells were infected with VSV-G-pseudotyped NL4-3-ΔE-EGFP (or the H13L tat derivative; 400 ng p24 per 106 cells) for 18 h. Real-time PCR was performed on cells collected 18 h p.i. to determine levels of viral DNA. Heat-killed virus serves as a control for residual plasmid contamination from transfection; mock infections were carried out with heat-killed virus under identical conditions. t tests were used to compare levels of viral DNA in Jurkat versus Jurkat-tat cells. Results represent mean ± standard deviation (SD) of results of two independent experiments. (B) Infections were carried out as for panel A. At 18 h p.i., cells were treated with TNF-α or control, and viral EGFP was measured by flow cytometry 24 h later. t tests were used to compare total (active + silent) infection levels for Jurkat versus Jurkat-tat cells (total infection = % GFP+ cells after TNF-α treatment; active infection = % GFP+ cells after control treatment; silent infection = active infection subtracted from total infection). Results represent mean ± SD of results of four independent experiments.