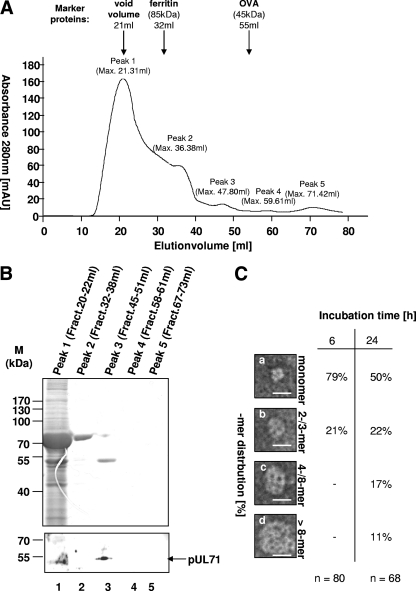
Fig 2.
Oligomerization potential of rpUL71. (A) Gel permeation chromatography analysis of rpUL71. rpUL71 purified in a single step was subjected to chromatography with a HiLoad 16/60 Superdex prep column using an ÄKTAFPLC system, and data were recorded at an absorbance of 280 nm. The column was calibrated with the following molecular mass markers: void volume (21 ml), ferritin (rs = 6.10 nm; elution volume, 32 ml), and ovalbumin (OVA; rs = 3.05 nm; elution volume, 55 ml). Five peaks were distinguished and termed peak 1 (maximum elution volume, 21.31 ml), peak 2 (maximum elution volume, 36.38 ml), peak 3 (maximum elution volume, 47.80 ml), peak 4 (maximum elution volume, 59.61 ml), and peak 5 (maximum elution volume, 71.42 ml). mAU, milli-absorbance units. (B) Analysis of the peak fractions by SDS-PAGE. The fractions peak 1 to peak 5 were separated by SDS-PAGE prior to Coomassie blue staining and immunoblot analysis with pAbUL71. Molecular mass markers are indicated on the left, and the position of rpUL71 is indicated on the right. (C) Electron microscopy analysis of purified rpUL71 from peak 3 negatively stained with 4% uranyl acetate. Molecular mass (in kilodaltons) can be calculated from particle size on the basis of the findings of Zipper et al. (49). Different high-molecular-mass forms of rpUL71, monomeric forms (a), dimers or trimers (b), and higher oligomeric forms (c and d), were obtained from the sample. The scale bars correspond to 20 nm. Incubation in phosphate buffer for 6 h led to predominantly monomeric forms (a) and dimers or trimers (b), but no higher-ordered structures (c and d) could be found. Incubation for 24 h led to predominantly monomeric forms (a), but dimers or trimers (b) and higher-ordered structures (c and d) could also be found.