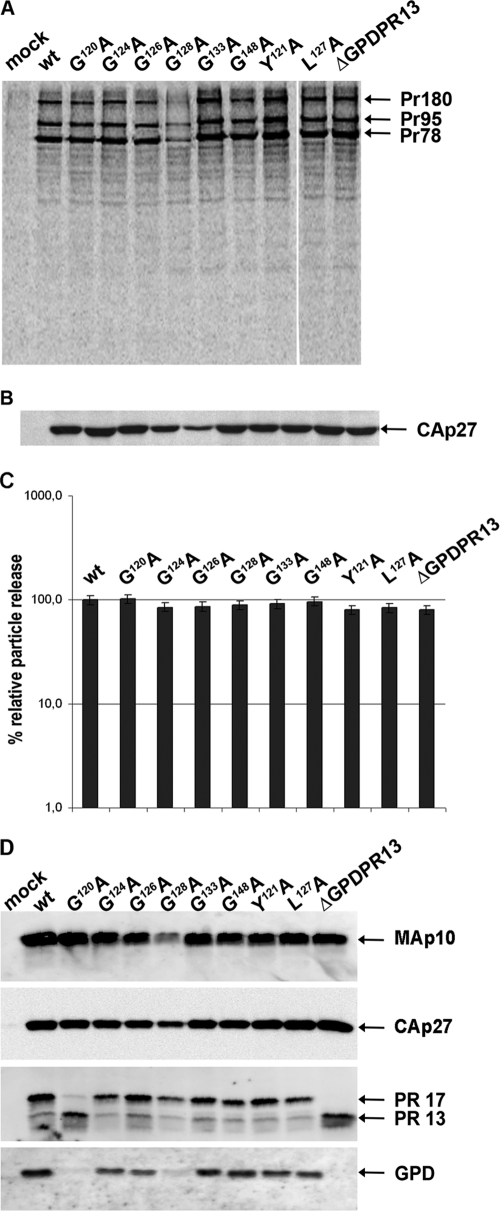
Fig 2.
Synthesis, release, and processing of wild-type M-PMV and GPD mutants. HEK 293T cells were transfected with wild-type or mutant M-PMV proviral DNAs. Viral proteins were metabolically labeled with [35S]cysteine-methionine mix for 30 min and then chased for 16 h. M-PMV CA(p27)-related proteins were then immunoprecipitated from the cells and culture media and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. (A) Intracellular M-PMV proteins Gag Pr78, Gag-Pro Pr95, and Gag-Pro-Pol Pr180 immunoprecipitated from the cell lysate after a 30-min pulse. (B) Released M-PMV CA(p27) immunoprecipitated from the culture medium 16 h after the chase. (C) Quantification of the release of wt M-PMV and GPD mutants. Band intensities of 35S-pulse-labeled Gag (Pr78) and released CA(p27) were calculated. The relative percentage of CA released into the culture medium was corrected for the intracellular expression of individual samples. (D) Western blot analysis of released wild-type and GPD-related mutant proteins. At 48 h after transfection of HEK 293T cells with wild-type and GPD mutant proviral DNAs, the VLPs from the culture medium were collected by centrifugation through a 20% sucrose cushion. The viral proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane, and detected by use of rabbit antibodies raised against (from top to bottom) MAp10, CA(p27), PR13, and the GPD.