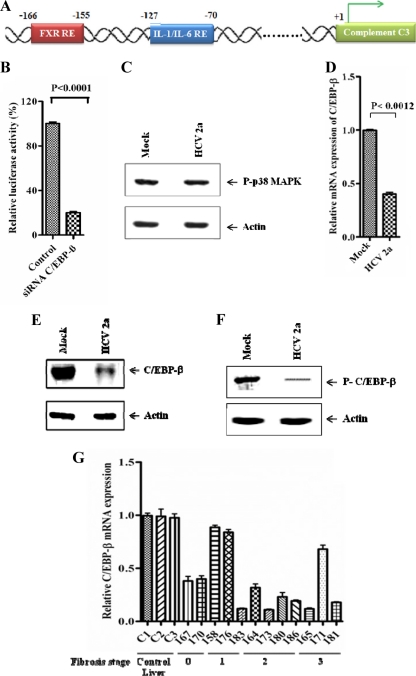
Fig 4.
HCV infection inhibits C/EBP-β expression. (A) Schematic view of human C3 promoter containing FXR and IL-1/IL-6 response elements. (B) Knockdown of C/EBP-β by siRNA attenuated IL-1β-induced C3 promoter activation in HepG2 cells. (C) Phospho-p38 MAPK levels remained unchanged in HCV genotype 2a-infected Huh 7 cells compared with uninfected controls. Cellular actin was used for comparison of protein load in each lane. (D) Reduction in C/EBP-β mRNA level in Huh7 cells infected with HCV genotype 2a, as estimated by real-time PCR. 18S RNA was used as an endogenous control. (E and F) Western blot analysis for total C/EBP-β and phospho-C/EBP-β in hepatocytes infected with HCV genotype 2a. Cellular actin was used for comparison of protein load in each lane. (G) C/EBP-β mRNA expression status in liver biopsy specimens from chronically HCV-infected patients in comparison to non-HCV-infected control liver tissues (C1, C2, and C3) by real-time PCR (P < 0.0001 as a group of experimental samples compared to controls by one-way ANOVA). Results were normalized to endogenous 18S RNA and are shown as individual samples organized according to the fibrosis stage of the patient liver.