Fig 6.
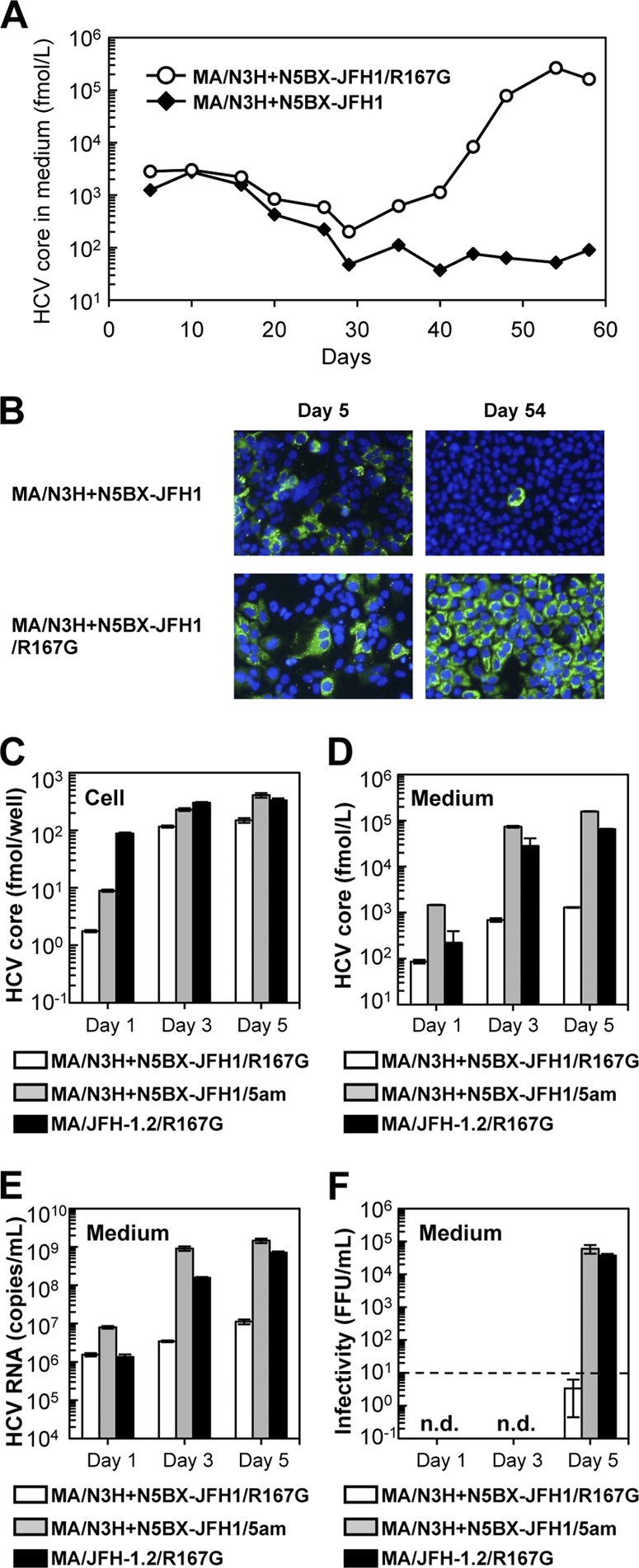
Cell culture-adaptive mutations enhanced infectious virus production of MA/N3H+N5BX-JFH1/R167G. (A) Long-term culture of MA/N3H+N5BX-JFH1 and MA/N3H+N5BX-JFH1/R167G RNA-transfected cells. Ten micrograms of HCV RNA was transfected into Huh7.5.1 cells, and cells were passaged every 2 to 5 days, depending on cell status. Culture medium was collected after every passage, and HCV core protein levels were measured. HCV core protein levels in culture medium from MA/N3H+N5BX-JFH1 and MA/N3H+N5BX-JFH1/R167G RNA-transfected cells are presented. (B) Immunostained cells on days 5 and 54 after transfection. Infected cells were visualized with anti-core antibody (green), and nuclei were visualized with DAPI (blue). (C to F) Effect of four additional cell culture-adaptive mutations on virus production. Ten micrograms of HCV RNA was transfected into Huh7.5.1 cells, and cells and medium were harvested on days 1, 3, and 5. HCV core levels in cells (C) and in medium (D) and HCV RNA levels in medium (E) were measured, and infectivity of medium (F) was determined. Assays were performed three times independently, and data are presented as means ± standard deviation. n.d., not determined. Dashed line indicates the detection limit.
