Fig 10.
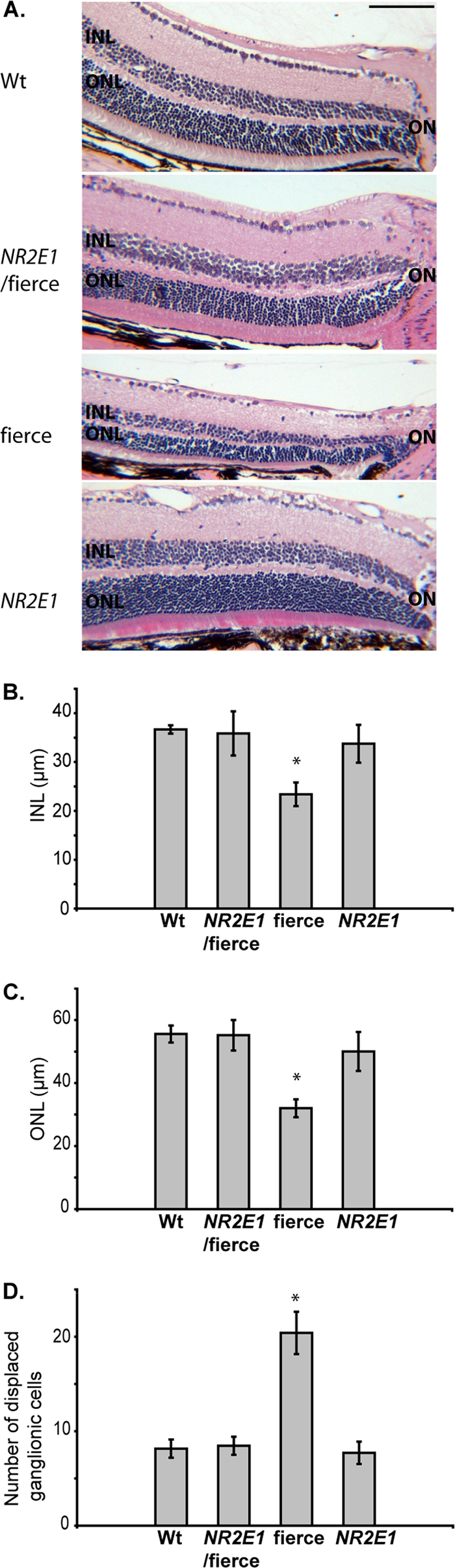
NR2E1/fierce mice were corrected for retinal architecture defects. (A) Hematoxylin-and-eosin-stained paraffin section analysis revealed that the retina of Wt, NR2E1/fierce, and NR2E1 mice appeared similar when the inner nuclear layer (INL) and outer nuclear layer (ONL) thicknesses were examined. Only the fierce retina demonstrated a reduction in the INL and ONL compared to results for the three other genotypes. ON, optic nerve. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (B) Quantitative analysis showed no significant difference when comparing the INL thicknesses of Wt, NR2E1/fierce, and NR2E1 mice. Only the fierce retina demonstrated a reduction in INL thickness compared to results for the three other genotypes (∗, P < 0.01). (C) No significant difference was found when comparing the ONL thicknesses of Wt, NR2E1/fierce, and NR2E1 mice. Only the fierce retina demonstrated a reduction in ONL thickness compared to the three other genotypes (∗, P < 0.05). (D) No significant difference was found when comparing the number of displaced ganglionic cells in the inner plexiform layer (IPL) of Wt, NR2E1/fierce, and NR2E1 mice. Only the fierce retina demonstrated increased displaced retinal ganglion cells in the IPL compared to results for the other three genotypes (∗, P < 0.01). (B, C, and D) The Kruskal-Wallis H test was performed on 4 to 6 mice for all genotypes. Error bars represent standard errors of the means.
