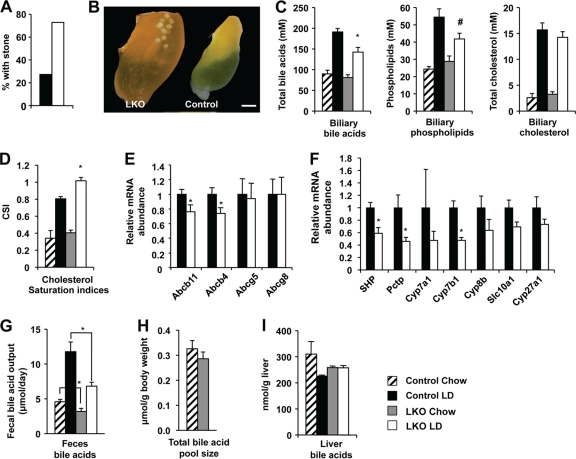
Fig 7.
Hepatic deletion of SIRT1 induces formation of cholesterol gallstones and impaired bile acid metabolism in mice upon a lithogenic diet feeding. (A) SIRT1 LKO mice display increased incidence of cholesterol gallstones (n = 11). The 9- to 10-month-old control and SIRT1 LKO mice were fed a lithogenic diet for 6 weeks. (B) Macroscopic appearance of gallbladders from control and SIRT1 LKO mice fed with the lithogenic diet for 6 weeks. Bar, 1 mm. (C) SIRT1 LKO mice display decreased biliary concentrations of bile acids and phospholipids (n = 8). *, P < 0.05; #, P = 0.068. (D) SIRT1 LKO mice have increased cholesterol saturation indices (CSI) in gallbladder bile (n = 8). *, P < 0.05. (E) SIRT1 deficiency reduces expression of bile acid and phospholipid transporters at the hepatocyte canalicular membrane (n = 11). *, P < 0.05. (F) Decreased expression of bile acid synthesis genes in the SIRT1 LKO mice (n = 11). *, P < 0.05. (G to I) SIRT1 LKO mice show decreased fecal bile acid output (G) but normal total bile acid pool size (H) and hepatic bile acids (I) (n = 5 to 6) *, P < 0.05.