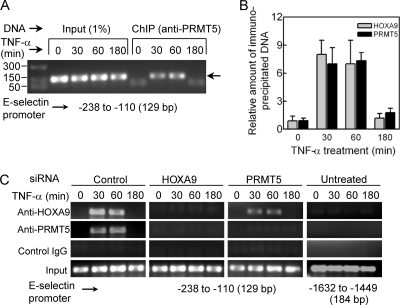
Fig 5.
To associate with the E-selectin promoter in TNF-α-treated EC, PRMT5 requires HOXA9. (A) PRMT5 transiently associates with the E-selectin promoter in response to TNF-α. ChIP assays were performed with the cross-linked chromatin from human EC both untreated and treated with TNF-α for 30, 60, or 180 min using anti-PRMT5 antibody. The specific E-selectin promoter region spanning bp −238 to −110 was amplified from the de-cross-linked immunoprecipitated DNA or input DNA by PCR with specific primer sets. The 129-bp products were analyzed by agarose-gel electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel and verified by sequencing. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown. (B) Relative enrichment of E-selectin promoter levels as measured by quantitative real-time PCR. Cross-linked chromatin was extracted from human EC treated with TNF-α for 0, 30, 60, or 180 min and precipitated with antibodies to either HOXA9 or PRMT5. The amplification of the specific E-selectin promoter region as shown above was monitored by real-time PCR. The recovered DNA was evaluated relative to DNA enriched by control IgG immunoprecipitation. Data represent the means ± SDs from three experiments. (C) HOXA9 is required for TNF-α-dependent PRMT5 association with the E-selectin promoter. ChIP assays were performed, using appropriate IgG as indicated, with human EC, untreated or treated with TNF-α for the indicated times, following a 24-h transfection with a negative control (Ambion, TX), HOXA9-specific, or PRMT5-specific siRNA. The PCR amplified DNA fragments were analyzed using a 2% agarose gel and sequenced for verification (data not shown). Data represent one of three replicate experiments.