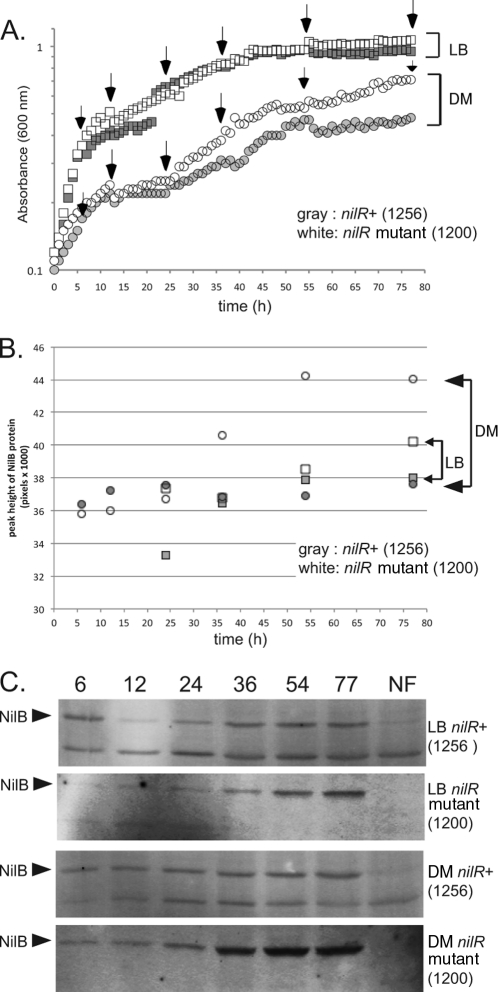
Fig 2.
NilB protein expression is highest in stationary phase, repressed by NilR, and elevated by growth in defined medium. (A) Growth curves of X. nematophila nilR+ and nilR mutant strains in defined medium (DM) and LB. White boxes and white circles represent the nilR mutant in LB and defined medium, respectively. Gray boxes and gray circles represent nilR+ in LB and defined medium, respectively. The growth curves of both strains are identical in LB. In defined medium, the curves are similar for the two strains, except that the nilR mutant reaches a higher A600 than the nilR+ strain in stationary phase. (B) Western blots of NilB protein expression. nilR+ and nilR mutant strains were grown in LB or DM as indicated. Crude cell extracts were taken at 6, 12, 24, 36, 54, and 77 h, total protein content was normalized, and samples were loaded onto 12% SDS-PAGE gels for anti-FLAG Western blotting. The arrows indicate NilB, and NF contains extracts from the equivalent X. nematophila strains lacking the FLAG tag. (C) Quantitation of the blots in panel B. White boxes and white circles represent levels of NilB detected in the nilR mutant strain when grown over time in LB and defined medium, respectively. Gray boxes and gray circles represent levels of NilB detected in the nilR+ strain when grown over time in LB and defined medium, respectively. Levels of NilB in LB are similar for the two strains; low levels of NilB are detectable at 6, 12, and 24 h (log phase), and maximal expression is at 54 and 77 h (stationary phase). Levels of NilB in the nilR+ strain grown in defined medium are similar to levels of NilB in LB, except that the amount of NilB expressed is constant over time. Maximum NilB levels are produced in the nilR mutant strain grown in defined medium; low levels of NilB are detectable at 6, 12, and 24 h (log phase), with an increase in expression at 54 and 77 h (stationary phase). Quantitation was done with ImageQuant IQTL 7.0.