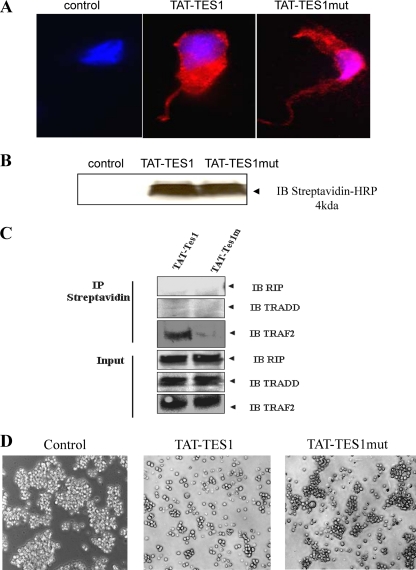
Fig 6.
Effects of synthetic peptides derived from LMP1 C-terminal sequences. (A) Monitoring of cellular uptake of peptides in HEK cells and subcellular localization. A total of 2 × 105 HEK cells were first plated and then incubated with 5 μM biotinylated TAT-TES1, TAT-TES1mut, or the vehicle only for 5 min. Then cells were labeled with Hoechst dye for nucleus detection, and phycoerythrin-labeled streptavidin was used for peptide detection. Cells were then analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. (B) HEK cells were incubated with each peptide as described above. Then the cells were lysed and analyzed by Western blotting using a streptavidin-horseradish conjugate for peptide detection. (C) HEK cells were incubated with peptides for 10 min; then cells were lysed. Peptides were immunoprecipitated with streptavidin coupled to Sepharose beads. Western blotting was then performed using antibodies against TRAF2, TRADD, and RIP to verify the abilities of peptides to interact with LMP1 signaling adaptors. (D) Effects of peptides on EBV-infected cell lines. NC5 cells were incubated with 15 μM each peptide for 10 h; then the mortality rates and induced phenotypes of cells were analyzed by photomicrography.