Fig 1.
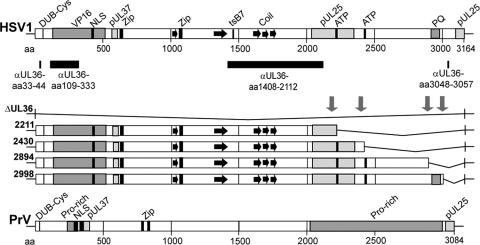
Primary sequence of HSV1 pUL36 and HSV1 UL36 mutants. The N-terminal third of HSV1 pUL36 harbors deubiquitinase and deneddylase activity with a conserved Cys at aa residue 65 (DUB-Cys), an NLS (aa 367 to 498), and binding sites for the major tegument protein VP16 and the inner tegument protein pUL37 (2, 37, 51, 53, 77, 114). The tsB7 mutation that prevents DNA release from incoming capsids at the nuclear pores has been mapped to aa 1453 in the middle of pUL36 (1). Furthermore, two potential leucine zipper motifs (Zip) at aa 632 to 653 and aa 1070 to 1091 and several coiled coils (black arrows) have been identified by in silico analysis (6, 61, 71, 103). Within the C-terminal third of HSV1 pUL36, there are two potential ATP binding motifs between aa 2211 to 2219 and 2430 to 2443, a prominent repeat of 35 PQ between aa 2911 to 2980, and two binding sites for pUL25 between aa 2037 to 2352 and 3102 to 3164 (16, 71, 92). The pUL36 regions against which polyclonal antibodies have been raised are indicated by black bars: a peptide of aa 33 to 44 at the N terminus (Nterm, pAb R28), recombinant protein fragments of aa 109 to 333 (pAb VP1-2 N) or aa 1408 to 2112 (middle, pAb 146 and pAb 147), and a peptide of aa 3048 to 3057 at the C terminus (Cterm, pAb R29) (49, 71, 116). Using the BAC pHSV1(17+)blueLox as a parental wild-type background (86), we have constructed HSV1(17+)blueLox-ΔUL36 lacking the entire UL36 open reading frame or inserted stop codons together with a kanamycin resistance cassette (downward-pointing arrows) upstream of the two potential ATP binding sites or up- and downstream of the prominent PQ repeat to generate the mutants HSV1(17+)blueLox-UL36codon2211stop, -2430stop, -2894stop, and -2998stop that express C-terminally truncated versions of pUL36. Similarly, PrV pUL36 also has a DUB-Cys at position 26, two NLSs, and a PrV pUL37 binding region, predicted leucine zippers at aa 779 to 800 and 827 to 848, several Pro-rich regions between aa 226 to 299 and 2026 to 3970, and a PrV pUL25 binding region at the very C terminus (8, 16, 51, 52, 56, 57, 81).