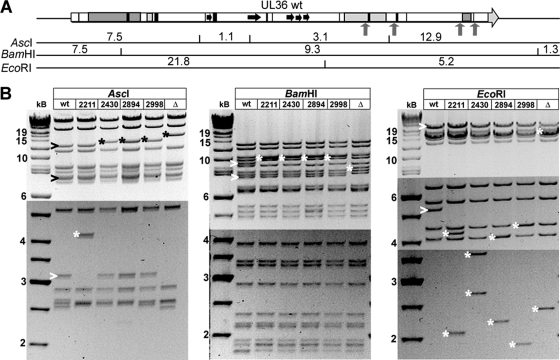
Fig 6.
Generation and characterization of pHSV1(17+)-UL36 mutants. (A) Using the BAC pHSV1(17+)blueLox as parental wild type (86), we have constructed pHSV1(17+)blueLox-ΔUL36 lacking the entire UL36 open reading frame. As further mutants, we have inserted stop codons together with a kanamycin resistance cassette (upward-pointing arrows) upstream of the two potential ATP binding sites or up- and downstream of the prominent PQ repeat and generated the BAC plasmids pHSV1(17+)blueLox-UL36codon2211stop, -UL36codon2430stop, -UL36codon2894stop, and -UL36codon2998stop to generate HSV1 strains expressing C-terminally truncated versions of pUL36. The expected fragment sizes after restriction digestions of the UL36 region with AscI, BamHI, or EcoRI were calculated according to the published HSV1(17+) sequence (GenBank accession no. NC_001806). (B) Agarose gels of restriction endonuclease digests of the parental pHSV1(17+)blueLox (wt); pHSV1(17+)blueLox-UL36codon2211stop, -UL36codon2430stop, -UL36codon2894stop, or -UL36codon2998stop; or pHSV1(17+)blueLox-ΔUL36 (Δ) with AscI, BamHI, or EcoRI. The sizes of the restriction fragments and molecular mass markers are indicated in kilobases. Altered fragments in the parental wt (>) and bands of the mutants shifted due to the insertion of the kanamycin resistance cassette with the stop codon (*) are indicated. The bands of various sizes of about 2.6 kb after AscI digestion most likely reflected the repetitive a-sequences that occur in various numbers in HSV1 genomes (86, 113).