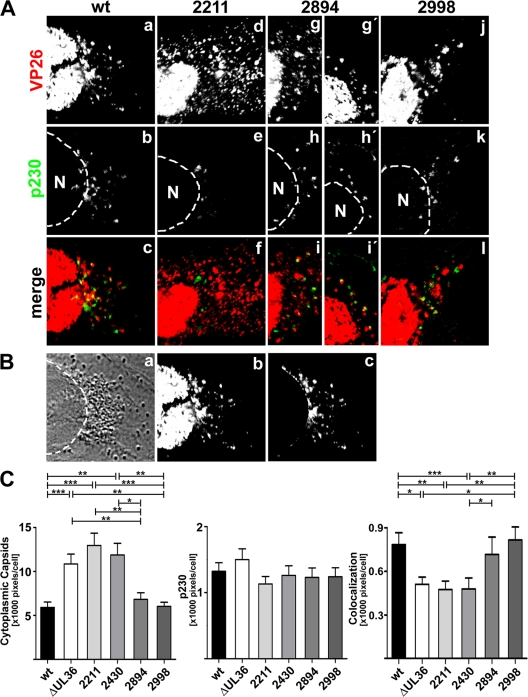
Fig 9.
Amino acids 2430 to 2893 of HSV1 pUL36 are required for capsid association with the trans-Golgi network. (A) Vero cells were infected at an MOI of 0.2 PFU/cell with pHSV1(17+)blueLox (wt; a to c) or the mutant HSV1(17+)blueLox-UL36codon2211stop (2211; d to f), -UL36codon2894stop (2894; g to i and g′ to i′), or -UL36codon2998stop (2998; j to l), transcomplemented with pUL36 by amplification on Vero-HS30 cells, and fixed at 15 h p.i. with 3% paraformaldehyde, followed by TX-100 permeabilization. The specimens were labeled with antibodies directed against VP26 (red and a, d, g, g′, and j; pAb) and a TGN marker protein (green and b, e, h, h′, and k; MAb p230) and analyzed by confocal fluorescence microscopy. (B) For quantification, the position of the nuclei was determined by differential interference contrast (a), and the nuclear but not the cytoplasmic VP26 signal (b) was digitally eliminated (c). (C) After infection with pHSV1(17+)blueLox (wt) or the mutants, the average number of cytoplasmic VP26-positive or p230-positive pixels and the degree of apparent colocalization were measured for each virus in 60 cells derived from two independent experiments. The error bars indicate the standard error of the mean. Significant differences according to a Mann-Whitney test are indicated: ***, P < 0.001; **, P = 0.001 to 0.01; *, P = 0.01 to 0.05.