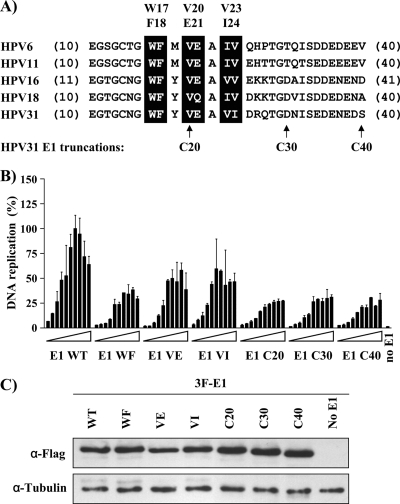
Fig 1.
The p80-binding domain of E1 is required for efficient HPV DNA replication. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of the p80-binding domains of E1 proteins from different anogenital HPV types. The residues highlighted in black are those mutated to alanines in the p80-binding mutants (WF, VE, and VI) of HPV31 E1. The boundaries of the different N-terminal truncations generated in HPV31 E1 (C20, C30, and C40) are indicated below the alignment by arrows. (B) DNA replication activities of 3F-E1 WT compared with the indicated E1 mutant proteins or truncated derivatives using a broad gradient of E1 expression vectors (0.625, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 25, 50, 75, and 90 ng). Cells transfected without an E1 expression plasmid were used as a negative control (no E1). Replication activity is reported as a percentage of the maximal signal obtained with WT E1. The error bars represent the standard deviations of duplicate values. The results are representative of at least three independent experiments. (C) Anti-Flag Western blot showing the expression of the different E1 proteins. β-Tubulin was used as a loading control.