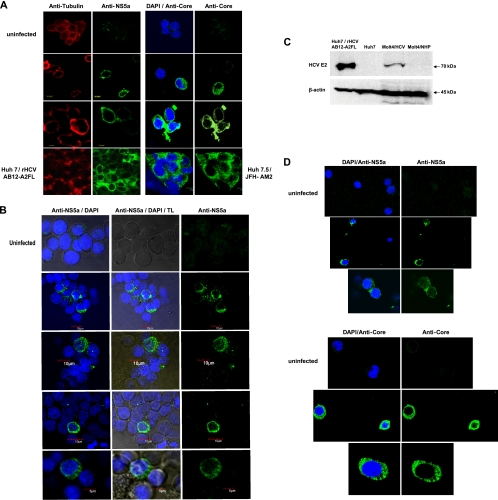
Fig 3.
Detection of HCV proteins in Molt4 and Jurkat T cells infected with wild-type HCV. (A) Detection of HCV NS5a and core proteins in Molt4 cells infected with HCV from patient 44/M by confocal microscopy. Uninfected Molt4 cells served as negative controls, while Huh7 cells transfected with HCV AB12-A2FL replicon and Huh7.5 cells infected with JFH-AM2 served as positive staining controls. The cells were counterstained with anti-tubulin MAb or DAPI. The images were captured at ×60 magnification. (B) Detection of cytoplasmic expression of HCV NS5a protein in Molt4 cells infected with different patient-derived HCV inocula by confocal microscopy. The cells were counterstained with DAPI to identify nuclei and examined under transmitted light (TL; center column) to visualize the cytoplasm. The images were captured at ×60 magnification. (C) Identification of HCV E2 protein in Molt4 cells infected with wild-type HCV by Western blotting using anti-E2 MAb. Huh7 cells carrying rHCV AB12-A2FL replicon were used as a positive control, while naïve Huh7 cells and Molt4 cells exposed to NHP served as negative controls. Detection of β-actin protein served as a loading control. (D) Detection of HCV NS5a and core proteins in Jurkat T cells infected with different patient-derived HCV inocula. Uninfected cells were used as a negative control. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. The images were captured at ×60 magnification.