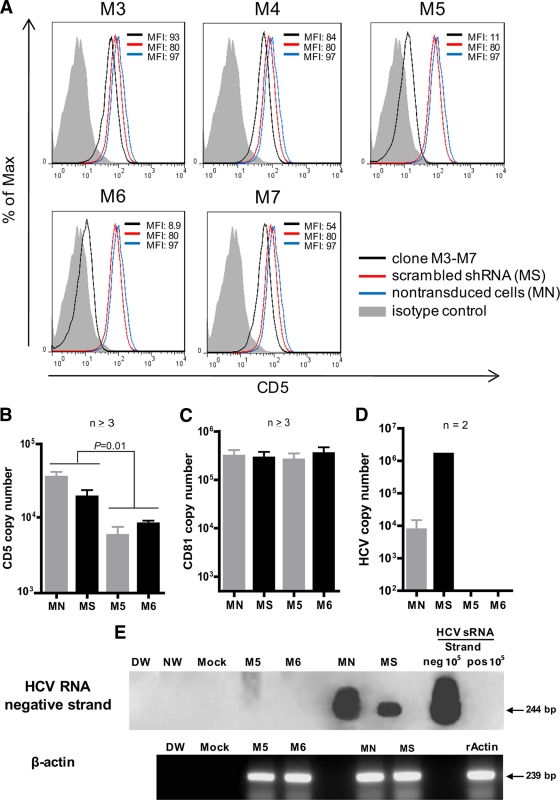
Fig 9.
Inhibition of CD5 expression in Molt4 cells makes them resistant to HCV infection. (A) Clones M-5 and M-6 of lentiviral particles carrying CD5 shRNA were most effective in knocking down CD5 protein, as revealed by flow cytometry with anti-CD5 antibody. (B and C) Inhibition of transcription of CD5 (B), but not CD81 (C), with clones M-5 and M-6 as quantified by real-time RT-PCR. (D) Molt4 cells transduced with clone M-5 or M-6, scrambled shRNA, or native cells were challenged with HCV from patient 44/M, and after 7 days of culture, the HCV released into the culture supernatant was quantified by real-time RT-PCR. (E) Replicating virus was identified by detection of the HCV RNA negative strand. Specificity and contamination controls were the same as those described in the legend to Fig. 2. β-Actin expression was used as a loading control and recombinant human actin (rActin) as a positive control. The error bars indicate SD.