Fig 1.
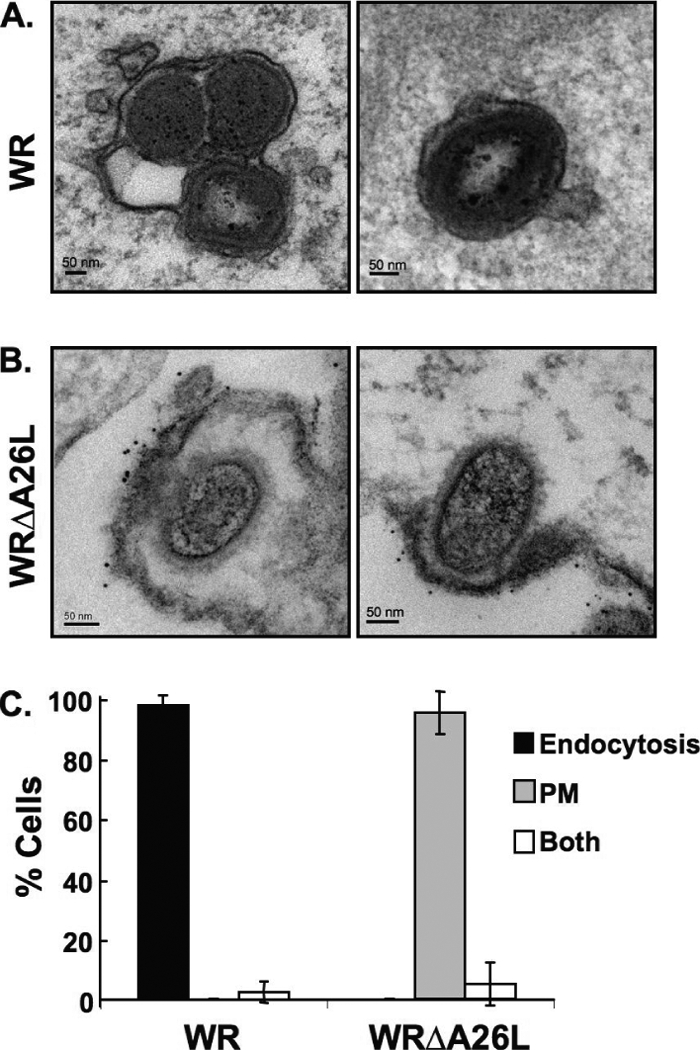
Immunogold electron microscopy analyses of HeLa cells infected with vaccinia virus MVs. (A) HeLa cells were infected with vaccinia virus wild-type WR and WRΔA26L MVs as described in Materials and Methods. After infection, cells were fixed and stained with anti-vaccinia virus MV primary antibody and goat anti-rabbit antibody conjugated to 6-nm gold particles and analyzed by EM. MV particles of wild-type strain WR are enclosed within intracellular vesicles. (B) HeLa cells were infected with WRΔA26L MVs and analyzed by EM as described in panel A. MV particles of WRΔA26L fused with the cell plasma membrane that were decorated with the immunogold-labeled antibody. (C) Quantification of cells (>30) infected with vaccinia virus MVs through different entry routes. Cells containing MV entry through endocytosis or plasma membrane fusion pathways were quantified as described in Materials and Methods. Data represent percentages of cells that contain MVs within intracellular vesicles (endocytosis), MVs fused with the plasma membrane (PM), or both.
