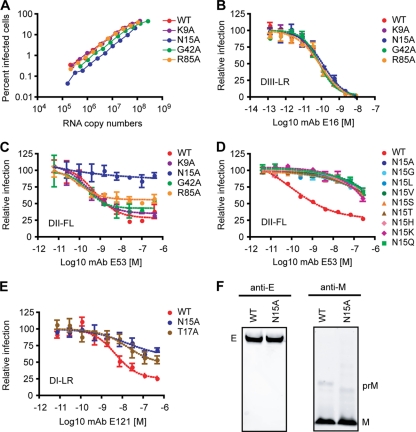
Fig 4.
Neutralization of prM mutants by monoclonal antibodies. PCR fragments containing K9A, N15A, G42A, and R85A mutations or the WT sequence were generated by using viral sequences cloned during the experiments described in the legend of Fig. 3 and ligated into pWNV-GFP-backbone to produce WNV-GFP viruses. (A) Specific infectivity of the WT virus and mutant viruses encoding K9A, N15A, G42A, or R85A prM mutations. Virus was harvested from culture supernatants at 72 h posttransfection, and titers were determined as described above. Infectivity is expressed as a function of the viral RNA content of DNase-treated virus stocks. (B and C) Determinations of the sensitivities of the WT and the K9A, N15A, G42A, and R85A mutants to neutralization by MAbs E16 (B) and E53 (C) were performed as described previously (57). Assays were performed with two independent virus stocks, and data are representative of a total of three independent experiments. (D) Sensitivity of the WT or the N15 variants to neutralization by MAb E53. Viruses were generated and titers were determined as described above for panel A. Sensitivity to MAb E53 neutralization was determined as described above. (E) Sensitivities of the WT and the N15A and T17A mutants to neutralization by MAb E121. Viruses were generated, titers were determined, and sensitivity to MAb E121 neutralization was determined as described above. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments. DIII-LR, E protein domain III lateral ridge; DII-FL, E protein domain II fusion loop; DI-LR, E protein domain I lateral ridge. (F) Western blot analysis for detection of WNV E, prM, and M proteins. WT and N15A viruses were harvested from infected BHK-21 cells, and the levels of WNV E, prM, and M proteins were determined by Western blotting using anti-E (MAb 4G2) and anti-M antibodies.