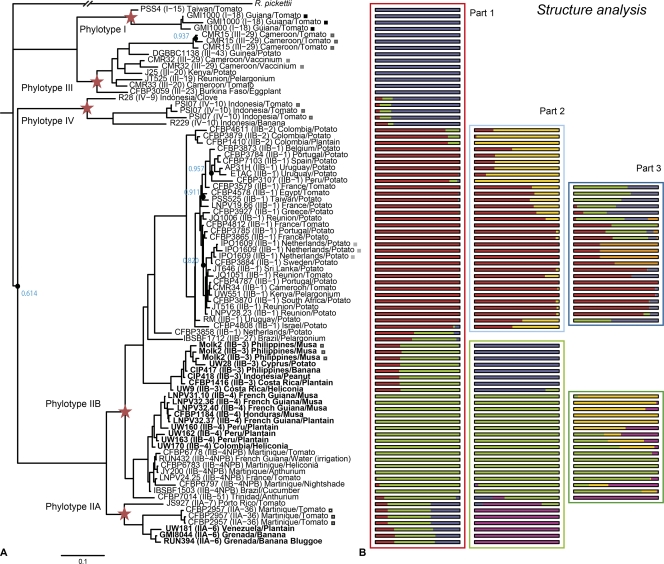
Fig 2.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of 72 Ralstonia solanacearum strains, computed by MrBayes, version 3.2. Blue numbers and black circles represent statistical support levels below 0.99; red stars indicate the main node for every phylotype. For each strain, the phylotype and sequevar (in parentheses) are given, along with the country and host of isolation. Moko disease strains are shown in boldface. Brown rot strains belong to phylotypes IIB-1 and IIB-2. Squares indicate repetitions of genomic DNA hybridization. (B) Population structure analysis. Each box represents an independent analysis of all R. solanacearum strains (box outlined in red), brown rot strains from phylotypes IIB-1 and IIB-2 (boxes outlined in light or dark blue), or Moko disease-causing strains from phylotypes IIA-6, IIB-3, and IIB-4 (boxes outlined in light or dark green). Within an analysis, each solid bar represents the proportions of ancestral nucleotides inherited from each of the inferred ancestral populations.