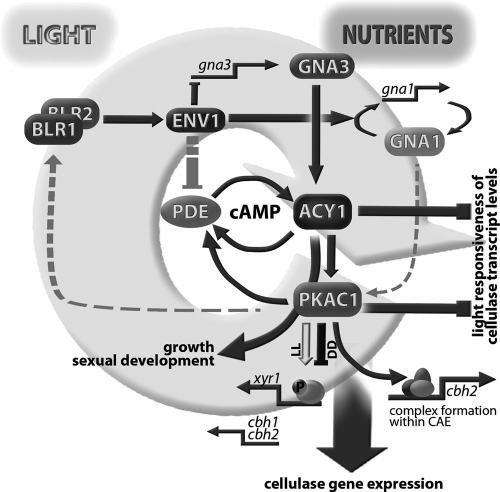
Fig 7.
Schematic representation of the functions of ACY1 and PKAC1 in integration of nutrient and light signals. Nutrient signals are transmitted by GNA1 and GNA3, activation of which leads to increased cAMP levels (53, 58). ENV1 enhances feedback regulation of gna1, acts negatively on transcription of gna3, and is assumed to dampen phosphodiesterase (PDE) function (69). ACY1 and PKAC1 decrease light responsiveness of cellulase transcript levels. Their effect on cellulase gene expression is mediated mainly by PKAC1, which alters protein complex formation within the cbh2 promoter and likely phosphorylates an upstream factor regulating xyr1 gene expression. Comparable effects of deletion of gna1 (58) and pkac1 suggest an additional level of regulation for the function of PKAC1 by GNA1, as proposed earlier (13). Fine-tuning of cross talk between light and nutrient signaling is likely to be accomplished by feedback of PKAC1 via the BLR1-BLR2 complex.