Figure 1.
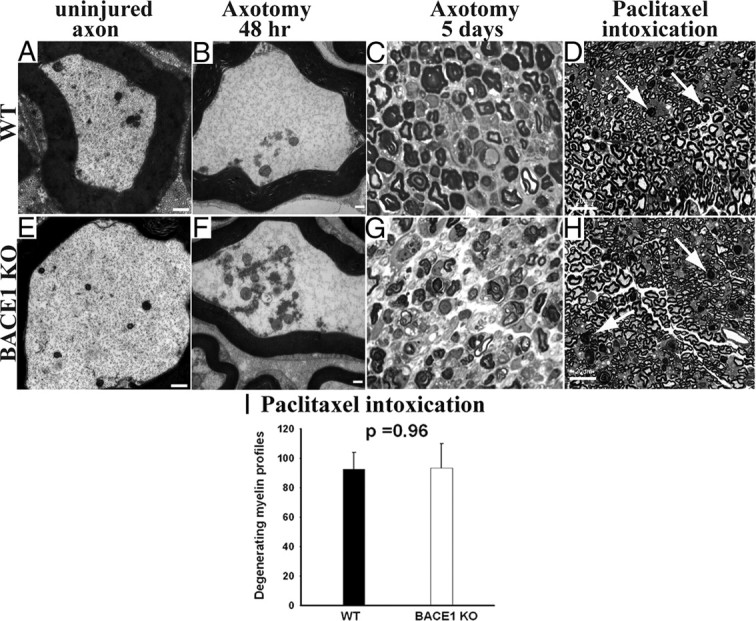
Similar degree of axonal and myelin degeneration in WT and BACE1 KO sciatic nerves after axotomy-induced Wallerian degeneration and intoxication with paclitaxel. A, B, E, and F are electron micrographs, and C, D, G, and H are semithin (1 μm) plastic sections stained with toluidine blue. A, Uninjured WT axon with normal axoplasm. B, WT at 48 h after crush showing conversion of the axonal cytoskeleton to granular debris. C, WT nerve at 5 d after crush showing degeneration of myelin. D, WT nerve intoxicated with paclitaxel. The arrows point to degenerating myelinated fibers. E, Uninjured BACE1 KO axon with normal axoplasm. F, BACE1 KO at 48 h after crush showing conversion of the axonal cytoskeleton to granular debris, similar to WT in B. G, BACE1 KO nerve at 5 d after crush showing degeneration of myelin. H, BACE1 KO nerve intoxicated with paclitaxel. The arrows point to degenerating myelinated fibers. I, Quantification of degenerating myelinated fibers in the whole cross-sectional area of nerves of mice intoxicated with paclitaxel. N = 3 per genotype. Values are mean ± SEM. Scale bars: A, B, D, F, 500 nm; C, F, G, H, 100 μm.
