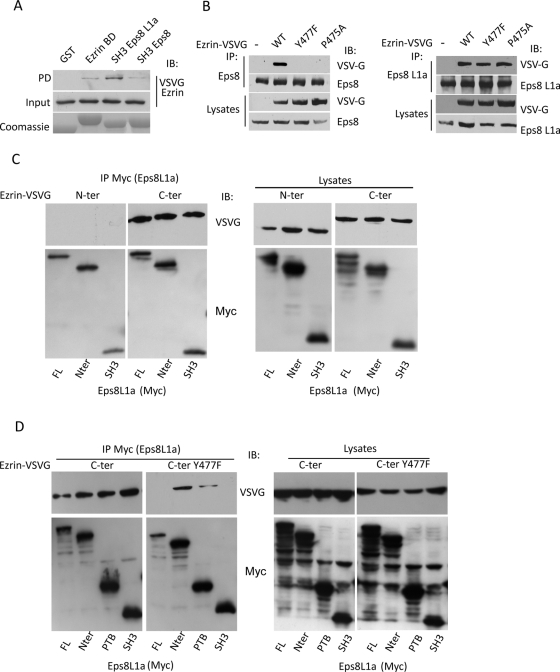
FIGURE 2:
Mapping of interaction sites between ezrin and Eps8 proteins. (A) Immobilized GST or GST fused to ezrin-binding domain on Eps8L1a (BD), the SH3 domain of Eps8L1a, and the SH3 domain of Eps8 were incubated with lysates of LLC-PK1 cells expressing ezrin-VSVG. Western blot was performed with an anti-VSVG antibody. Bottom, the Coomassie staining of GST-fused proteins. (B) Left, immunoprecipitation performed with an anti-Eps8 antibody on lysates of LLC-PK1 cells stably transfected with the empty vector (–) or with cDNA coding ezrin wild type (WT), ezrinY477F, or P475A tagged with VSVG. Immunoblots were performed with an anti-VSVG antibody to detect ezrin. Eps8 interacts only with wild-type ezrin. Right, the immunoprecipitation was performed as before, but with an anti-Eps8L1a antibody. Eps8L1a interacts with wild-type ezrin, as well as with ezrin Y477F and ezrin P475A. (C) 293T cells were cotransfected with cDNA coding the VSVG-tagged carboxy-terminal (C-ter) or amino-terminal (N-ter) domains of ezrin and Myc-tagged full-length Eps8L1a (FL) or its various domains. Left, immunoprecipitation performed with an anti-Myc antibody, followed by an immunoblot on immunoprecipitated proteins with anti-Myc and anti-VSVG antibodies. Right, cell lysates analyzed with anti-VSVG and anti- Myc antibodies. (D) 293T cells were cotransfected with cDNA coding the VSVG tagged carboxy-terminal domain of ezrin carrying or not the mutation Y477F and Myc-tagged full-length Eps8L1a or its various domains. Left, immunoprecipitation performed with an anti-myc antibody, followed by Western blots with anti-VSVG and anti-Myc antibodies. Right, cell lysates analyzed with anti-VSVG and anti-Myc antibodies. The introduction of the Y477F mutation in the carboxy-terminal domain of ezrin abolishes the interaction of Eps8L1a SH3 domain with ezrin.