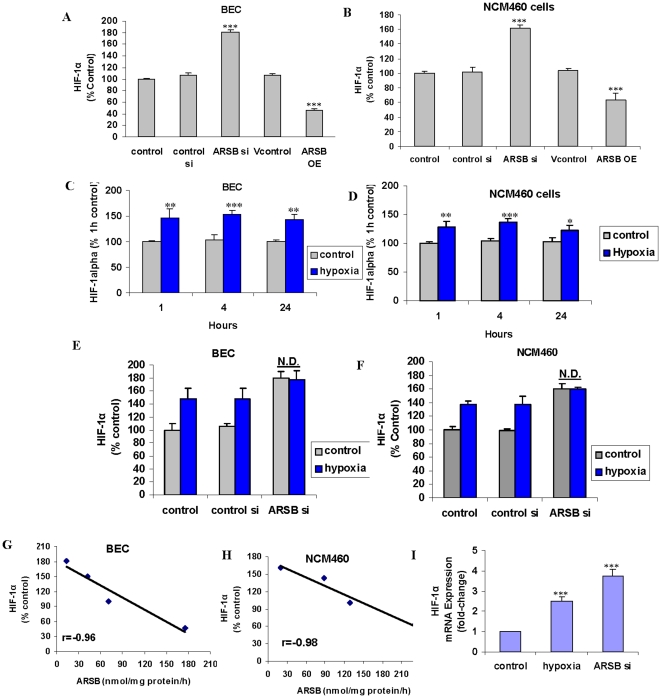
Figure 4. Nuclear HIF-1α levels were increased by ARSB silencing and reduced by ARSB overexpression in BEC and NCM460 cells, and HIF-1α mRNA expression was increased by ARSB silencing in BEC.
A. Activation of HIF-1α was significantly increased by silencing ARSB and significantly reduced by overexpression of ARSB in the BEC (p<0.001). B. In the NMC460 cells, ARSB silencing significantly increased the activation of HIF-1α and overexpression significantly reduced HIF-1α activation in the NCM460 cells (p<0.001). C. In the BEC, the effects of hypoxia (10% O2) on HIF-1α activation were significant at 1 h (p<0.01), 4 h (p<0.001), and 24 h (p<0.01), with the maximum increase at 4 h. D. As in the BEC, in the NCM460 cells, the effects of hypoxia (10% O2) on HIF-1α activation were significant at 1 h (p<0.01), 4 h (p<0.001) and 24 h (p<0.05), with the maximum increase at 4 h. E. In the BEC, the combined effects of ARSB silencing and hypoxia (10% O2) for 24 h had no greater effect on activation of HIF-1α than ARSB silencing alone. F. Similarly, in the NCM460 cells, the combined effects of ARSB silencing and hypoxia (10% O2) for 24 h had no greater effect on the activation of HIF-1α than ARSB silencing alone. G, H. The ARSB activity at baseline, following ARSB overexpression, following ARSB silencing by siRNA, and following hypoxia (10% O2)×24 h were inversely correlated with the nuclear HIF-1α levels in the BEC and the NCM460 cells (r = −0.96; r = −0.98, respectively). I. HIF-1α mRNA expression increased to 2.5 (±0.23) times the baseline following 10% oxygen×4 h and to 3.73 (±0.34) times the baseline following ARSB silencing by siRNA×24 h (p<0.001) in the BEC. [ARSB = arylsulfatase B; BEC = bronchial epithelial cell; HIF = hypoxia inducible factor].