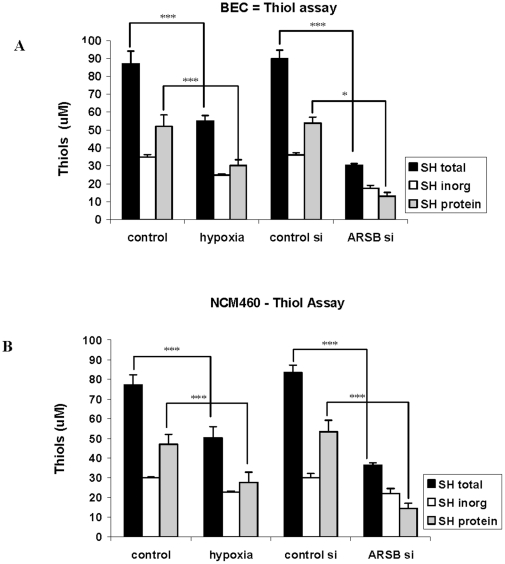
Figure 6. ARSB silencing and hypoxia reduce the total cellular sulfhydryl content.
A. Overall decline in the total cellular sulfhydryl content in the BEC followed both hypoxia (10% O2×4 h) and ARSB silencing, consistent with the observed effect on the reduced glutathione and the overall change in the cellular redox state (p<0.001). Total sulfhydryl content is composed of inorganic and protein thiols, and the inorganic thiol did not change significantly, indicating that the change in total thiols was attributable to the protein-associated thiols. B. Similar decline in the thiol cellular sulfhydryl content occurred in the NCM460 cells following either hypoxia (10% O2×4 h) or ARSB silencing (p<0.001). The inorganic thiol content did not change significantly, indicating that the change occurred in the protein thiol component. [BEC = bronchial epithelial cell; ARSB = arylsulfatase B].