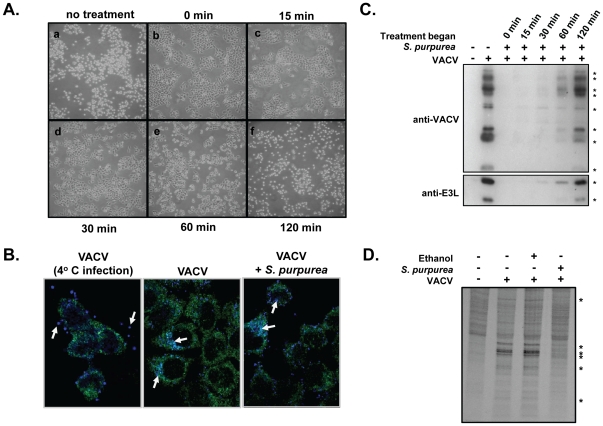
Figure 2. The effect of S. purpurea extracts on VACV induced CPE and protein synthesis.
A and C) HeLa cells were infected with VACV at an MOI = 10 followed by the addition of 25 microL S. purpurea extract/ml media immediately (0 min) or at 15, 30, 60 or 120 min post infection. ‘No treatment’ cells received ethanol/glycerol carrier only. For (A), at 6 HPI, the cell monolayers were photographed. For (C), at 3 HPI, cell lysates were prepared and the VACV E3L protein or total VACV proteins detected by Western blot. * indicate the position of VACV proteins and the VACV-E3L protein. Duplicate experiments were done at 6 HPI (not shown) B) Hela cells were infected with a VACV construct expressing cyan fluorescent protein fused to the viral A5 core protein. In the first panel, the infection was maintained at 4°C. For the middle and last panel, the infection was done at 37°C, in the absence or presence of S. purpurea, respectively. D) HeLa cells were mock infected or infected with VACV at an MOI = 10 followed by the addition of 25 microL S. purpurea extract/ml media or ethanol/glycerol carrier. At 4 HPI, the cell monolayers were radiolabelled with [35S]-methionine, cell lysates prepared, proteins separated by SDS-PAGE, and visualized by autoradiography. * indicate the position of VACV proteins.