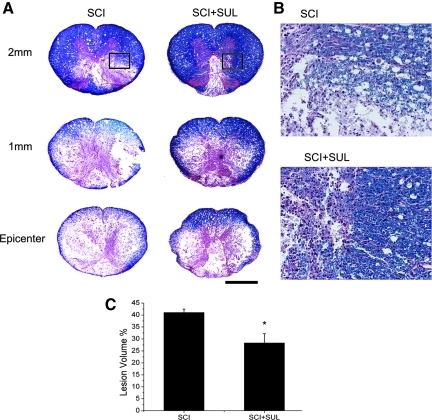
FIG. 6.
Sulforaphane (SUL) improves histopathological outcomes and decreases spinal cord lesion volume. (A) Representative cross sections of spinal cords stained with hematoxylin-eosin and luxol fast blue of sulforaphane-treated and untreated animals at 1 week after SCI. Sections correspond to the injury epicenter and sites 1 and 2 mm rostral to the epicenter. (B) Enlarged area corresponding to inset in (A) demonstrates that animals treated with SUL had smaller areas of shrunken neurons in gray matter and reduced white matter degeneration. (C) Areas of degeneration were quantified for lesion volume by Neurolucida software. Lesion volume analysis indicates that SUL-treated animals have lower lesion volume when compared to control groups. Data are expressed as mean±SEM; *p<0 .05, n=6 per group. Bar=50μm.