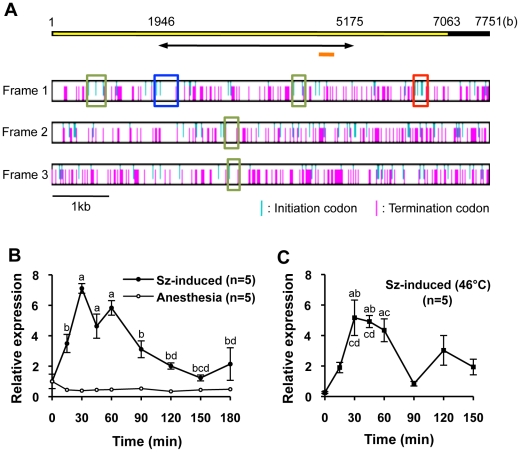
Figure 1. Identification and characterization of Acks, the Japanese honeybee kakusei homolog, as a non-coding IEG.
(A) Overview of Acks cDNA and open reading frame (ORF) analysis. The yellow bar and black bar represent the Acks cDNA region highly conserved among the Acks and kakusei cDNAs and the region adjacent to the Acks cDNA, respectively. The arrow indicates the region corresponding to the putative neural activity-inducible Acks transcript. The orange bar indicates the region corresponding to sense and antisense probes used in the in situ hybridization. Horizontal boxes under the upper yellow and black bar indicate open reading frame analysis in each reading frame of the Acks cDNA, respectively. The blue and pink bars present in each box indicate positions of initiation and termination codons, respectively. Colored squares on the horizontal boxes indicate potential ORFs longer than 150b. The blue (in Frame 1) and red box (in Frame 1) indicate the longest ORF and the ORF conserved among Acks and kakusei cDNAs, respectively. (B) Time course of Acks expression level investigated by quantitative RT-PCR after seizure induction under room temperature (25°C). Values are means ± SEM (a, different from 0 min P<0.01; b, different from 30 min P<0.01; c, different from 45 min P<0.01; d, different from 60 min P<0.01; Tukey-Kramer's test). Sz-induced, seizure-induced. (C) Time course of Acks expression level investigated by quantitative RT-PCR after seizure induction under the high temperature (46°C). Values are means ± SEM (a, different from 0 min P<0.01; b, different from 15 min P<0.05; c, different from 90 min P<0.01; d, different from 150 min P<0.05; Tukey-Kramer's test).