Fig. 2.
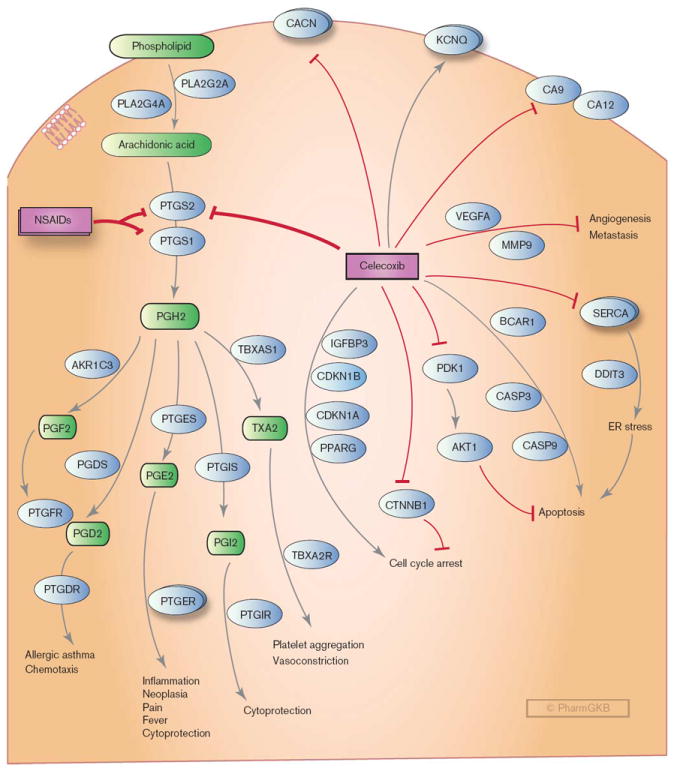
Stylized cell depicting the mechanism of action of celecoxib and candidate genes interacting with celecoxib and involved in the proposed anticancer mechanisms of celecoxib, including induction of apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, regulation of angiogenesis, and induction of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. CACN: L-type calcium channels; KCNQ: voltage-gated potassium channels; MMP9, metalloproteinase; NSAIDs, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; PGH2, prostaglandin H2; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; PGI2, prostacyclin; PGD2, prostaglandin D2; PGF2, prostaglandin F2; PTGER, prostaglandin E receptors; SERCA, sarcoplasmic/ER calcium ATPases; TXA2, thromboxane A2; VEGFA, vascular endothelial cell growth factor. A fully interactive version is available online at http://www.pharmgkb.org/pathway/PA152241951.
