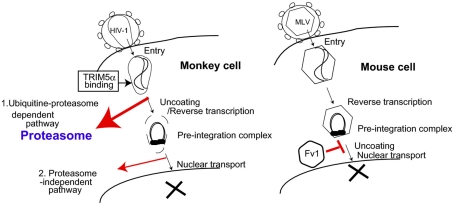
Figure 1.
Proposed models of TRIM5α and Fv1 restriction pathways. (Left) Proteasome-dependent and -independent pathways of TRIM5α-mediated human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) restriction in monkey cells. 1. Ubiquitin–proteasome-dependent pathway. Oligomerized TRIM5α recognizes the incoming HIV-1 core. Subsequently, TRIM5α is polyubiquitinated, and ubiquitinated TRIM5α along with HIV-1 core complex are degraded in the proteasome (bold red arrow). 2. Proteasome-independent pathway. Direct binding of TRIM5α with HIV-1 core causes destruction of the viral core without any cellular factors (thin red arrow). (Right) Fv1 inhibits nuclear transport of pre-integration complex of murine leukemia virus (MLV). The precise mechanism of Fv1-mediated restriction is unclear.