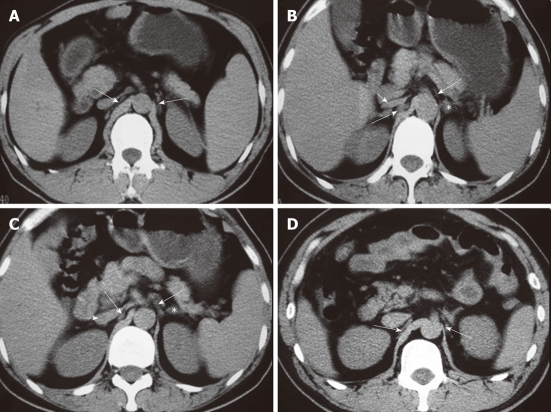
Figure 12.
Computed tomography images show the celiac ganglia at different levels. A: A celiac ganglion (long arrows) at the root of the superior mesenteric artery; its density is the same as the liver and spleen or slightly less than the diaphragma crura; B: The celiac ganglia (long arrows) at the level of the pancreatic head and neck. The left celiac ganglia were lamina-shaped and located lengthwise in the space in the front of the left adrenal gland (*); the right celiac ganglia were a thick, line-shaped structure dorsal to the inferior vena cava (IVC) and lateral to the right diaphragma crura; C: A celiac ganglion (long arrows) at the level of the root of the celiac trunk. It appeared lamina- and nodule-shaped; D: The celiac ganglia (long arrows) at the level of the uncinate process, with well-defined margins. The left ganglia were lamina-shaped and located lengthwise in the space to the front and the left of the adrenal gland (*); the right ganglia were thick and line-shaped, located dorsal to the IVC and lateral to the right diaphragma crura. Short arrows indicate IVC (B, C).