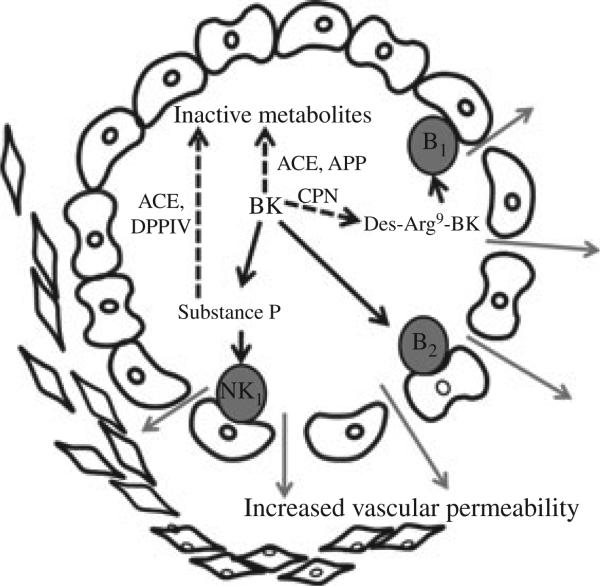
Figure 4.
Bradykinin increases vascular permeability directly by stimulating its B2 receptor and indirectly by stimulating the release of substance P from nerve terminals. Bradykinin degradation by carboxypeptidase N (CPN) produces an active metabolite, des-Arg9- BK, which stimulates the B1 receptor. Substance P induces vascular permeability by stimulating neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptors. Bradykinin and substance P are degraded by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). During ACE inhibition, bradykinin and substance P are degraded primarily by aminopeptidase P (APP) and dipeptidyl peptidase IV, respectively.