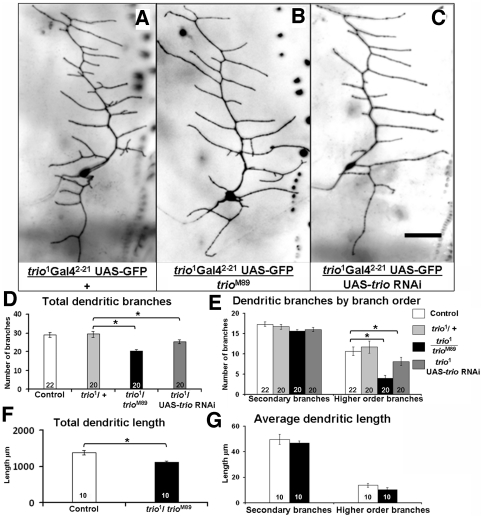
Figure 2. trio mutations affect dendritic branching of Class I vpda neurons cell autonomously.
a–c) A vpda neuron from a wandering third instar larvae of (a) trio 1 Gal42–21UAS-GFP/+ (control), (b) trio 1Gal42–21UAS-GFP/trio M89 and (c) trio 1Gal42–21UAS-GFP/UAS-trio RNAi; scale bar 50 µm. d–e) Quantification of dendritic branching in control, trio mutant and UAS-trio RNAi expressing vpda neurons. d) Dendritic branching of vpda neuron: trio knockdown reduces number of dendritic branches, e) average number of branches per branch order of vpda neuron: trio knockdown affects number of only higher order branches. f–g) Quantification of dendritic length in control and trio mutant vpda neuron. f) Total dendritic length of vpda neuron: trio mutations reduce total dendritic length g) average dendritic length per branch order of vpda neuron: trio mutations do not affect average dendritic length. The number of samples (n value) for each genotype is indicated by the number inside the respective bar, error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM) and asterisks indicate p value<0.05.