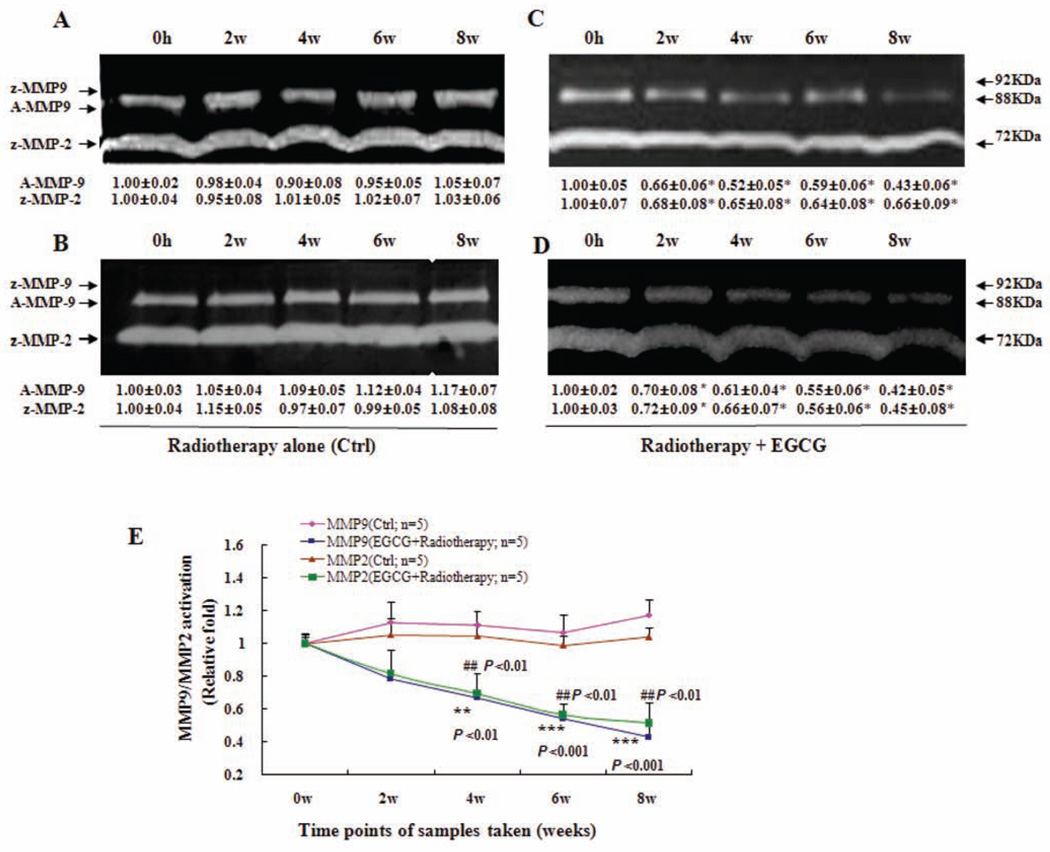
Fig. (3).
Inhibition of activation of serum MMP9/MMP2 by orally-administrated EGCG in breast cancer patients under radiotherapy. The blood samples were obtained as described in Fig. 2 legend. MMP9/MMP2 activation in sera was analysed using zymography. In (C) and (D), breast cancer patients Z and J received three oral doses of EGCG (400 mg) daily for 8-w during the 5-w radiotherapy cycles and 3-w afterwards. In (A) and (B) The breast cancer patients X, and Y in control group received radiotherapy alone during the 8-w without EGCG treatment. The activation of serum MMP9/MMP2 zymogens (z-MMP9/z-MMP2; Mr 72,000 and Mr 92,000 gelatinase activities) and active MMP9 (A-MMP9; Mr 88,000) was determined by gelatin zymography analysis. Values (the relative activation of serum active MMP9 and MMP2 zymogens) are shown as mean ± SD (Bar) of 3 runs for each sample, only one set of gels is shown. In (E), the activation of serum A-MMP9/z-MMP2 zymogens in the blood samples of all the patients was analyzed by gelatin zymography and statistical analysis. As described above, all the serum samples were from both the breast cancer patients (n=5) received EGCG treatment for 8-w under the radiotherapy and the breast cancer patients (n=5) in control group who received radiotherapy alone during the 8-w without EGCG treatment. Statistical analysis was done using the ANOVA and Bonferroni test. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001 (n=3).