Figure 1.
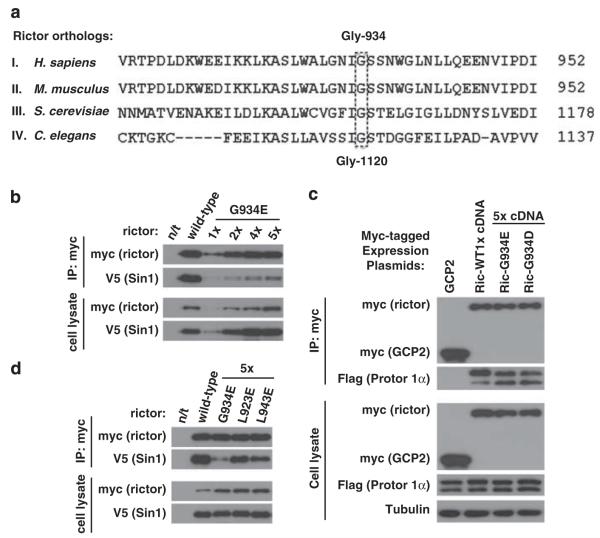
The rictor Gly-934 amino-acid residue is crucial for the rictor/Sin1 interaction. (a) Alignment of the rictor ortholog sequences. The C. elegans rictor Gly-1120 site aligns with the human rictor Gly-934 residue. The rictor orthologs carrying the following accession numbers have been analyzed: I. H. sapiens (AAS79796.1), II. M. musculus (NP_084444.3), III. S. cerevisiae (DAA07754.1) and IV. C. elegans (F29C12.3). The rictor sequences were obtained from National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database and were analyzed by the BLAST protein alignment tool. (b) Rictor G934E mutation interferes with rictor/Sin1 interaction. The wild-type or mutated myc-tagged rictor plasmid was transiently co-expressed with the Sin1-V5 plasmid in 293T cells. In order to overcome the low expression of the mutant form, the cDNA plasmid levels applied for transfection were increased as indicated. Following 48 h after transfection, cells were lysed as described previously (Chen et al., 2011) in the 40 mm 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (pH 7.5), 120 mm NaCl, 1 mm ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid(EDTA), 10 mm Na-pyrophosphate, 10 mm Na-glycerophosphate, 50 mm NaF and 1% Triton X-100 buffer supplemented with protease inhibitors (Roche, Indianapolis, IN, USA). The scraped lysates were incubated for 20 min at 4 °C to complete lysis. The soluble fractions of cell lysates were isolated by centrifugation at 16 000 g at 4 °C for 15 min. For immunoprecipitation, 4 μg of c-myc antibody (Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) were added to the cleared cellular lysates, containing 1 mg of total protein, followed by incubation with rotation at 4 °C for 90 min. After 1 h incubation with 45 μl of the 25% protein G-agarose slurry (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA), immunoprecipitates were washed four times with lysis buffer and analyzed for indicated proteins by immunoblotting as described previously (Chen et al., 2011). The mutated form of rictor displays a low binding to Sin1 in comparison with wild type. (c) Similar study has been performed and analyzed as in (a), where myc-rictor and its mutants have been co-expressed with the Flag-tagged Protor 1α. (d) The Leu-923 and Leu-943 sites of rictor are not crucial for the rictor/Sin1 interaction. The L923E and L943E myc-tagged rictor mutants were transiently expressed together with Sin1-V5 in 293T cells. To reach equal to the wild-type rictor level of expression, the same optimization as in (b) was performed. The cells were lysed and the assembled complexes were immunopurified as described in (b).