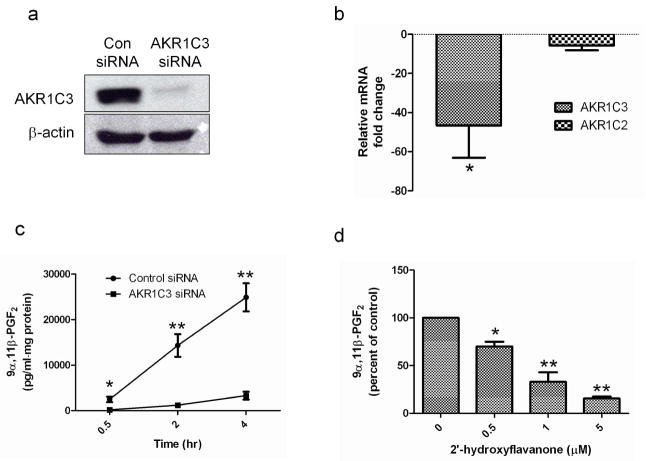
Figure 3. AKR1C3 siRNA and 2HFN attenuate AKR1C3 enzymatic activity.
(a) PHK transfected with 10nM of AKR1C3 or non-specific siRNA (Con siRNA) were allowed to differentiate for 48 hours and AKR1C3 protein was evaluated by western blot (n=3). (b) To examine AKR1C3 siRNA specificity, cells were treated as described in (a), mRNA was extracted and the transcription of AKR1C3 and AKR1C2 was evaluated by RT-PCR (means ± SEM, n=4, *P<0.05). (c) PHK were treated with AKR1C3 or control siRNA, allowed to differentiate for 48 hours and AKR1C3 enzymatic activity was evaluated at intervals by assessing 9α,11β-PGF2 in supernatants using ELISA (means ± SEM, n=4, *P<0.05, **P<0.01). (d) 2HFN dose-dependently reduced AKR1C3 activity in PHK, as determined by ELISA quantification of 9α,11β-PGF2 levels in supernatants, 2 hours post treatment (n=4, *P<0.05, **P<0.01).