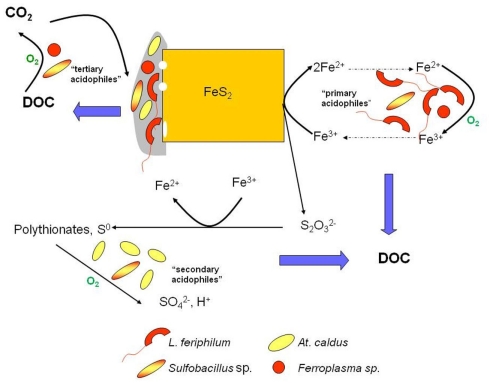
Figure 7.
The oxidative dissolution of pyrite in acidic liquors, showing the major microorganisms identified in the biooxidation of refractory gold concentrates and the bioleaching of a cobaltiferous pyrite concentrate processed at ca. 40°C. Those reactions that consume oxygen are indicated; “DOC” is dissolved organic carbon.