Figure 4.
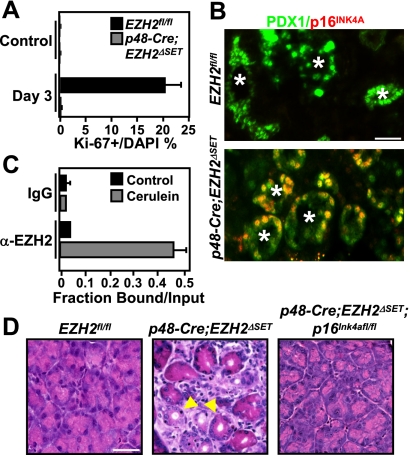
EZH2 is required for the proliferative expansion step during pancreatic regeneration. (A) Quantification of Ki67-positive cells at day 3 after final cerulein injection shows a proliferation defect in p48-Cre;EZH2ΔSET pancreata. Results represent the means±SD of three independent determinations in two mice per genotype. (B) Double immunofluorescence analysis of p16INK4A and PDX1 demonstrates that p16INK4A is suppressed in the PDX1-positive metaplastic epithelium (marked by asterisks) in EZH2fl/fl but not p48-Cre;EZH2ΔSET pancreata. Images shown are representative of data obtained from three mice per genotype. Bar, 50 μm. (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis of the p16Ink4a locus in EZH2fl/fl pancreata harvested at day 3 after the final cerulein injection demonstrates recruitment of EZH2 to the p16Ink4a promoter during regeneration. Results represent the means±SD of three independent determinations in two mice per genotype. (D) Pancreata from EZH2fl/fl, p48-Cre;EZH2ΔSET, and p48-Cre;EZH2ΔSET;p16Ink4afl/fl mice were harvested on day 9 following the final cerulein injection. H&E-stained sections show that impaired regeneration is rescued in p48-Cre;EZH2ΔSET;p16Ink4afl/fl pancreata. Selected metaplastic lesions are indicated by arrowheads. Images shown are representative of data obtained from three animals per genotype. Bar, 50 μm.