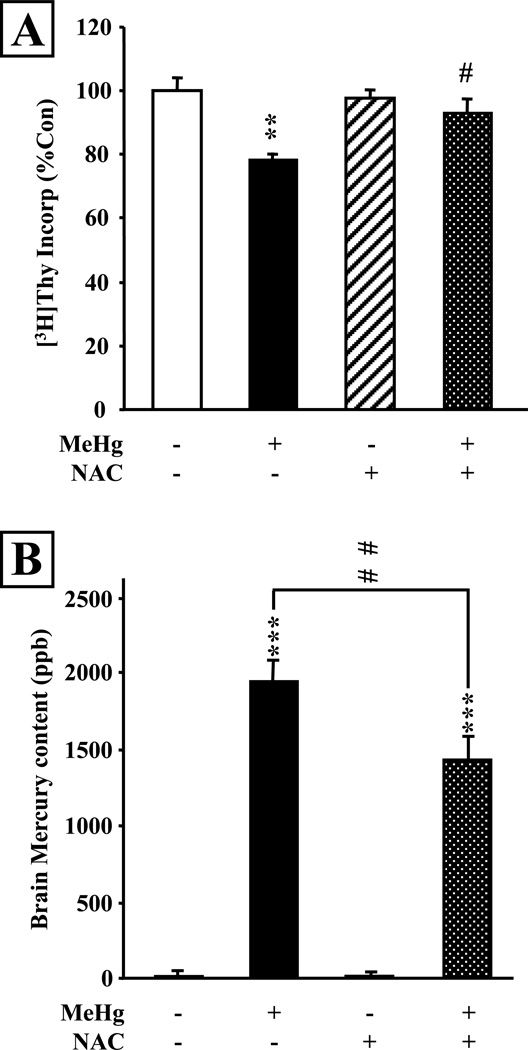
Figure 2. NAC administration reduces mercury uptake into the hippocampus and prevents inhibition of DNA synthesis in developing P7 rats in vivo.
P7 rats were injected with saline or MeHg (5µg/gbw) and received 5 repeated injections of NAC (10µg/gbw per injection) over 8 hours with 2 hours intervals between each injection. NAC exposure was initiated 2 hours before MeHg exposure. A: [3H]-Thy incorporation into the whole hippocampus was measured 24 hours after MeHg exposure. The inhibitory effect of MeHg on DNA synthesis was almost completely abolished by NAC. B: ICP-MS measurement of hippocampal mercury content 24 hours after treatment with NAC and/or MeHg. Mercury was almost undetectable in the control and NAC treated animals. MeHg sc injection led to a massive Hg uptake into the hippocampus, which was significantly reduced by NAC. Values are expressed as the means ± sem of 4 independent experiments for all groups, with 3 animals per group in each experiment (N=12 per group). **, P < 0.01 vs control; ***, P < 0.001 vs control; #, P < 0.05 vs MeHg; ##, P < 0.01 vs MeHg.