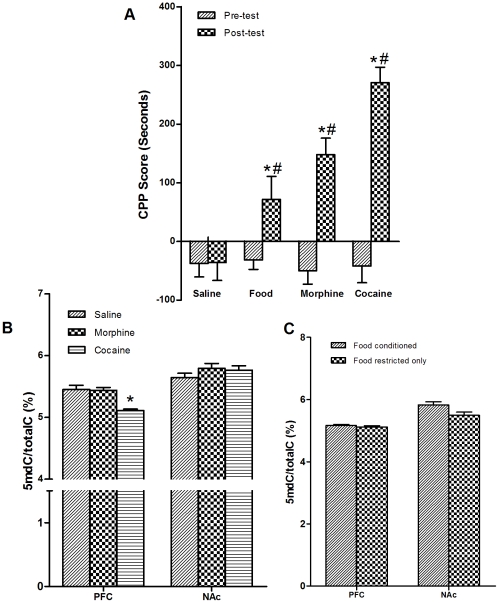
Figure 1. Changes in global DNA methylation by cocaine-, morphine-, and food-CPP.
(a) Establishments of food-, morphine- and cocaine-CPP. *p<0.05, postconditioning in comparison with preconditioning within the same group; # p<0.05 in comparison with saline group during postconditioning (n = 16 for saline; n = 20 for food; n = 18 for morphine, and n = 18 for cocaine); (b) Changes of global DNA methylation level in the PFC, and in the NAc following cocaine- and morphine CPP. *p<0.05 in comparison with saline group (n = 16 for saline; n = 9 for morphine and cocaine); (c) Food-CPP training did not change the global DNA methylation (n = 10). Data are depicted as the percentage of methylated cytosine in total cytosine. Data are expressed as mean±SEM.