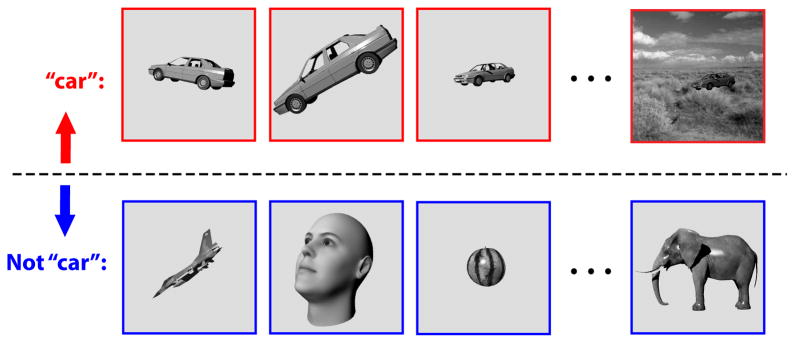
Figure 1. Core object recognition.
is the ability to rapidly (<200 ms viewing duration) discriminate a given visual object (e.g., a car, top row) from all other possible visual objects (e.g. bottom row) without any object-specific or location-specific pre-cuing (e.g. (DiCarlo and Cox, 2007). Primates perform this task remarkably well, even in the face of identity-preserving transformations (e.g., changes in object position, size, viewpoint, and visual context).