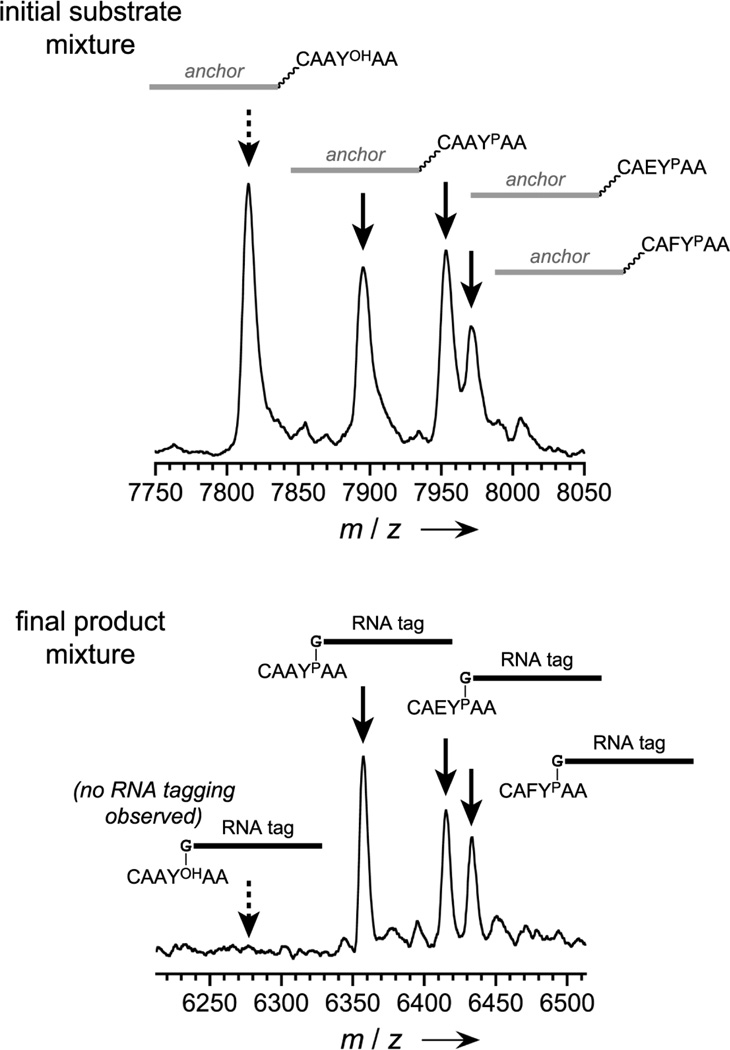
Figure 4.
Analysis of a peptide mixture by mass spectrometry using the DNA-catalyzed tagging approach. See diagram of this experiment in the Supporting Information. Each of a mixture of nonphosphorylated and phosphorylated peptides (100 pmol nonphosphorylated peptides; 33 pmol each of three phosphorylated peptides) was attached via HEG tether to a common DNA oligonucleotide anchor, and the mixture was tagged with RNA by 8VP1. After PAGE separation of RNA-tagged peptides and removal of the DNA anchors by DTT reduction, analysis by MALDI mass spectrometry revealed that only the phosphorylated peptides were covalently modified with the RNA tag, as desired. No tagging of the nonphosphorylated peptide was observed (lower spectrum, left side; compare with substantial nonphosphorylated peptide signal in the upper spectrum).