Figure 4. Residual mtDNA Nucleoids are Removed from EndoG Mutant Sperm During Spermatid Individualization.
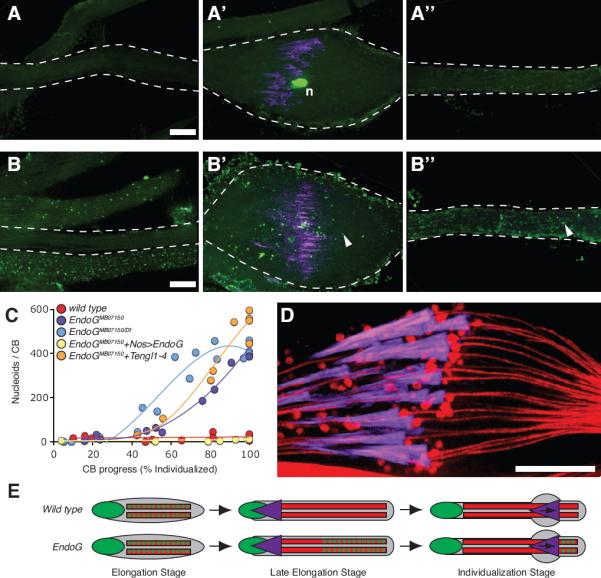
(A–A”,B–B”) Two individualizing sperm-tail bundles stained for DNA (green) and actin (purple). EndoGMB07150/+ (A–A”) and EndoGMB07150/Df (B–B”) bundles imaged ahead of the cystic bulge (A”, B”), at the cystic bulge (A', B') and behind the cystic bulge (A, B). Arrowheads indicate examples of mtDNA nucleoids. Scale bars are 10 μm. (C) Number of nucleoids in cystic bulges at different stages of individualization in bundles from control and EndoG mutants. (D) Focal section through a wild type cystic bulge stained for mitochondria (DJ–GFP: red) and actin (purple). (E) Schematic showing early mtDNA elimination in wild type and late mtDNA elimination in EndoG mutant spermatids; DNA (green), mitochondria (red), and investment cones (purple).
