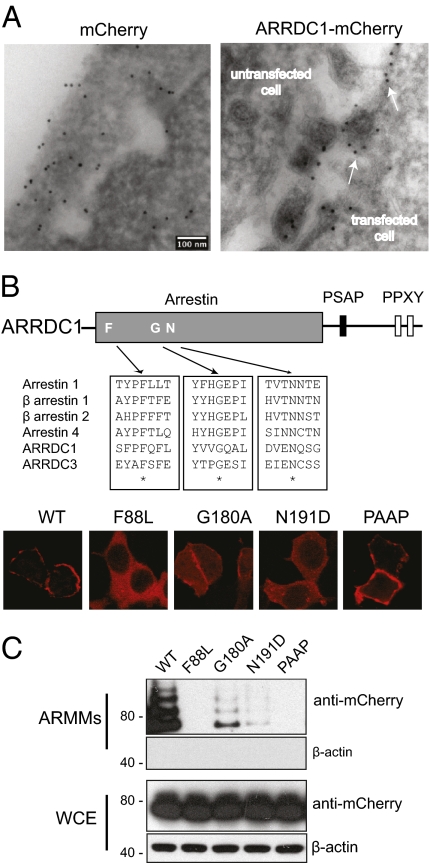
Fig. 4.
Arrestin domain-mediated association of ARRDC1 with the plasma membrane is essential for cell surface-derived budding of ARMMs. (A) ARMMs bud at the cell surface. Cryosections of HEK293T cells transfected with constructs expressing mCherry or ARRDC1-mCherry were immunogold labeled with anti-mCherry. White arrows (Right) indicate presumptive sites of outward budding at the cell membrane adjacent to immunogold-positive ARMMs captured from the intercellular space. An untransfected cell is indicated in the same field and shows no staining. (Scale bar, 100 nm.) (B) Disruption of conserved arrestin residues alters localization of ARRDC1. Conserved arrestin-domain residues among arrestins 1–4 and the known membrane-associated ARRDC1 and ARRDC3 were identified by ClustalW alignment and were mutated. The corresponding mCherry fusion mutants were expressed in HEK293T cells and showed altered localization compared with wild-type or PAAP ARRDC1. (C) HEK293T cells were transfected with constructs expressing the indicated ARRDC1 mutants fused to mCherry. The corresponding ARMMs and whole-cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies.