Fig. 10.
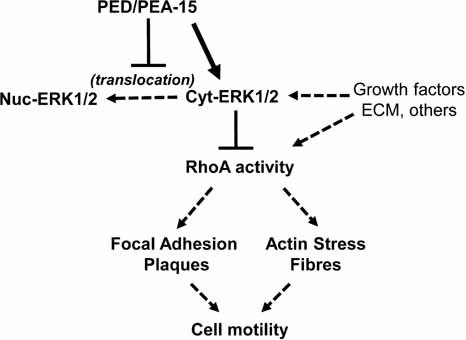
Schematic representation of PED/PEA-15 effect on cytoskeletal organization and cell motility. Many growth factors, extracellular matrix proteins, and other extracellular signals induce ERK1/2 activation and translocation from cytosol (Cyt-ERK1/2) to nucleus (Nuc-ERK1/2), as well as RhoA activity and cytoskeletal rearrangements allowing cellular motility. When PED/PEA-15 is hyper-expressed, it binds ERK1/2 and prevents nuclear translocation, thereby causing accumulation into the cytosol. This is paralleled by a decrease of RhoA activity, which most likely affects the formation of FAPs and stress fibers. In cells overexpressing PED/PEA-15, biochemical and morphological changes are also accompanied by an overall reduced cellular motility.
