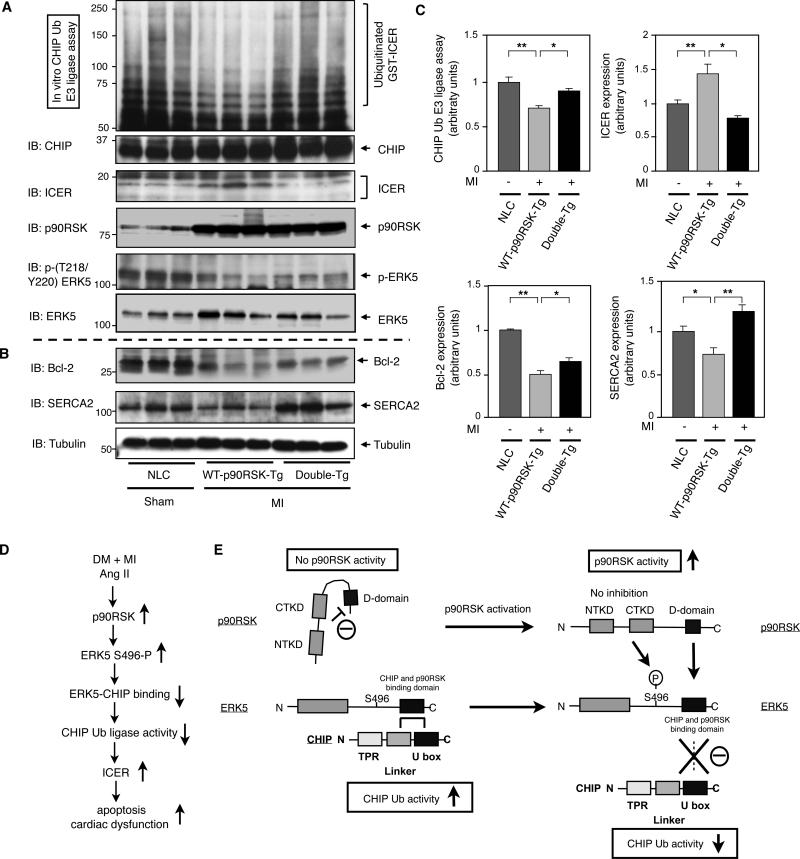
Figure 8. CHIP Ub ligase activity and ICER expression after MI in NLC, WT-p90RSK-Tg, and Double-Tg mice.
(A-C) Heart samples from control and MI groups in NLC, WT-p90RSK-Tg, and Double-Tg mice were collected and CHIP Ub ligase activity assay was performed as described in methods (top). Western blot shows (A) CHIP, ICER, p90RSK, p-ERK5, and ERK5 and (B) Bcl-2, SERCA2, and tubulin expression. (C) Quantifications of relative CHIP Ub ligase activity and ICER expression (upper), Bcl-2 and SERCA2 expression (lower) as described in Fig.2B and Fig.1B. (**p<0.01, * p<0.05, mean±S.D., n=3). (D) A model of DM + MI or Ang II-mediated p90RSK-ERK5-CHIP signal transduction pathway that regulates cardiac apoptosis and subsequent cardiac dysfunction. (E) A scheme depicting p90RSK-mediated regulation of the ERK5-CHIP module. At the basal level, inactive p90RSK inhibits the D-domain to bind with ERK539. p90RSK-free ERK5 associates with CHIP at its linker and U-box domain and maintains its CHIP Ub ligase activity to prevent ICER induction and subsequent apoptosis13. However, once p90RSK gets activated, the inhibition of the kinase domain is released39, and the D-domain of p90RSK associates with the ERK5 COOH-terminal domain, leading to compete with ERK5-CHIP association and ERK5-S496 phosphorylation, which disrupts ERK5-CHIP interaction. The disruption of ERK5-CHIP interaction inhibits CHIP Ub ligase activity13, increases ICER induction, and induces apoptosis13, 10.